|
NeuZephyr
Simple DL Framework
|
 |
NeuZephyr
Simple DL Framework
|
Momentum optimizer for deep learning models. More...
Public Member Functions | |
| Momentum (Tensor::value_type learning_rate, Tensor::value_type beta) | |
| Constructs a Momentum optimizer with a specified learning rate and momentum factor. | |
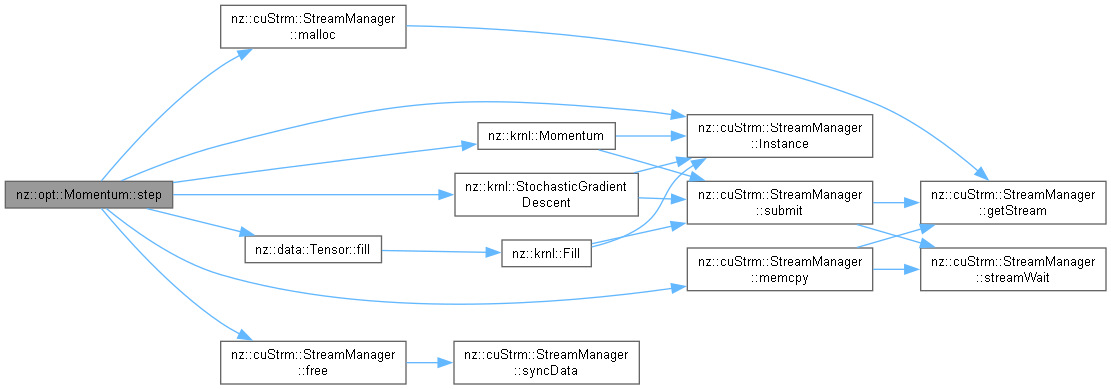
| void | step (Node *input) override |
| Performs a single optimization step using the Momentum algorithm. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from nz::opt::Optimizer Public Member Functions inherited from nz::opt::Optimizer | |
| Optimizer ()=default | |
| Default constructor for the Optimizer class. | |
| virtual | ~Optimizer ()=default |
| Default destructor for the Optimizer class. | |
Momentum optimizer for deep learning models.
The Momentum class implements the Momentum optimization algorithm, which is a variant of the Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD). Momentum helps accelerate SGD in the relevant direction and dampens oscillations, improving convergence speed and stability. It achieves this by incorporating a velocity term that accumulates a fraction of the previous gradients, which is used to update the model parameters in the direction of the accumulated gradients.
This class extends the Optimizer base class and provides a concrete implementation of the step method, which updates the model's parameters (represented as Node objects) using the Momentum algorithm.
velocity map, which tracks the velocity (accumulated gradients) for each model parameter (Node).Node objects, and each node must have associated gradients.Node object, and if a Node does not have an existing velocity, it is initialized to a zero tensor.Definition at line 352 of file Optimizer.cuh.
|
explicit |
Constructs a Momentum optimizer with a specified learning rate and momentum factor.
This constructor initializes a Momentum optimizer with a given learning rate and momentum factor. The learning rate controls the step size in the gradient descent update, while the momentum factor helps accelerate the optimizer by incorporating previous gradients.
| learning_rate | The learning rate for the optimizer, which determines the step size for parameter updates. |
| beta | The momentum factor, which controls the influence of previous gradients on the current update. Typically a value between 0.0 and 1.0, where a value closer to 1 means more influence from previous gradients. |
Node objects and that these nodes will have gradients available when the step method is called.Definition at line 21 of file Optimizer.cu.
|
overridevirtual |
Performs a single optimization step using the Momentum algorithm.
The step function updates the model parameters represented by the Node object using the Momentum optimization algorithm. It incorporates both the current gradients and the previous velocity term to update the model parameters. The momentum term helps accelerate the convergence of the optimizer by smoothing out updates and reducing oscillations.
This method performs the following steps:
Node if it is not already available. The velocity vector stores the running average of past gradients, scaled by the momentum factor.| input | A pointer to the Node object representing the model parameters. This object should have gradients stored in its output attribute, which will be used to update the parameters. |
Node object is assumed to have a valid output tensor with its gradients already computed.Node to ensure the momentum is correctly applied per parameter.beta) to control the influence of past gradients on the current update.Implements nz::opt::Optimizer.
Definition at line 26 of file Optimizer.cu.