|
NeuZephyr
Simple DL Framework
|
 |
NeuZephyr
Simple DL Framework
|
Expands tensors with batch size 1 to arbitrary batch dimensions through data replication. More...
Public Member Functions | |
| ExpandNode (Node *input, Tensor::size_type newBatch) | |
| Constructs an ExpandNode object. | |
| void | forward () override |
| Performs the forward propagation for the ExpandNode. | |
| void | backward () override |
| Performs the backward propagation for the ExpandNode. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from nz::nodes::Node Public Member Functions inherited from nz::nodes::Node | |
| virtual void | print (std::ostream &os) const |
| Prints the type, data, and gradient of the node. | |
| void | dataInject (Tensor::value_type *data, bool grad=false) const |
| Injects data into a relevant tensor object, optionally setting its gradient requirement. | |
| template<typename Iterator > | |
| void | dataInject (Iterator begin, Iterator end, const bool grad=false) const |
| Injects data from an iterator range into the output tensor of the InputNode, optionally setting its gradient requirement. | |
| void | dataInject (const std::initializer_list< Tensor::value_type > &data, bool grad=false) const |
| Injects data from a std::initializer_list into the output tensor of the Node, optionally setting its gradient requirement. | |
Expands tensors with batch size 1 to arbitrary batch dimensions through data replication.
The ExpandNode class enables batch dimension expansion by replicating single-instance input data across the batch dimension. This operation is particularly useful for converting single-sample processing networks into batch-processing configurations without modifying core network architecture.
Core operational characteristics:
Implementation mechanics:
Common application scenarios:
Critical operational constraints:
| nz::nodes::calc::ExpandNode::ExpandNode | ( | Node * | input, |
| Tensor::size_type | newBatch ) |
Constructs an ExpandNode object.
| input | A pointer to the input Node. Memory location: host. |
| newBatch | The new batch size for the output tensor. Memory location: host. |
This function constructs an ExpandNode object. It first checks if the batch size of the input tensor is 1. If not, it throws an std::invalid_argument exception. Then, it adds the input node to the list of inputs, creates a new output tensor with the specified new batch size and the same dimensions as the input tensor except for the batch size, and sets the node type to "Expand".
Memory management strategy: The function allocates memory for the output tensor using std::make_shared. The memory will be automatically managed by the smart pointer and freed when it goes out of scope. Exception handling mechanism: If the batch size of the input tensor is not 1, the function throws an std::invalid_argument exception with an appropriate error message.
| std::invalid_argument | If the input tensor's batch size is not 1. |
|
overridevirtual |
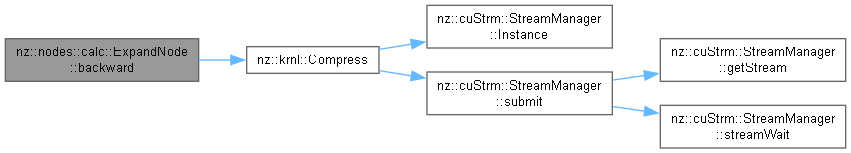
Performs the backward propagation for the ExpandNode.
| None |
This function performs the backward propagation of the ExpandNode. It first checks if the input tensor requires gradient computation. If it does, it calculates the size of a single element in the input tensor (excluding the batch dimension) and the total number of elements in the output tensor. Then, it configures the CUDA grid and block dimensions for parallel execution. Finally, it calls the Compress kernel function to perform the compression operation on the gradients, which is the reverse operation of the forward expansion.
Memory management strategy: The function does not allocate or free any memory directly. It relies on the memory allocated for the input and output gradient tensors. Exception handling mechanism: There is no explicit exception handling in this function. However, the Compress kernel call may encounter errors related to CUDA operations such as invalid grid/block dimensions or device issues.
| None |
Compress kernel function should be implemented correctly to handle the gradient compression operation.Compress kernel, but in general, it has a linear time complexity O(n), where n is the total number of elements in the output tensor.Implements nz::nodes::Node.
Definition at line 594 of file Nodes.cu.
|
overridevirtual |
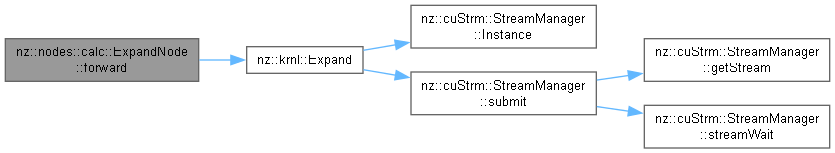
Performs the forward propagation for the ExpandNode.
| None |
This function conducts the forward propagation of the ExpandNode. It first calculates the size of a single element in the input tensor (excluding the batch dimension) and the total number of elements in the output tensor. Then, it configures the CUDA grid and block dimensions for parallel execution. Finally, it calls the Expand kernel function to perform the actual expansion operation on the device.
Memory management strategy: The function does not allocate or free any memory directly. It relies on the memory allocated for the input and output tensors in the constructor. Exception handling mechanism: There is no explicit exception handling in this function. However, the Expand kernel call may encounter errors related to CUDA operations such as invalid grid/block dimensions or device issues.
| None |
Expand kernel function should be implemented correctly to handle the expansion operation.Expand kernel, but in general, it has a linear time complexity O(n), where n is the total number of elements in the output tensor.Implements nz::nodes::Node.
Definition at line 585 of file Nodes.cu.