 |
NeuZephyr
Simple DL Framework
|
 |
NeuZephyr
Simple DL Framework
|
A class for representing and manipulating multidimensional arrays (tensors) in GPU memory. More...
Public Member Functions | |
Constructors and Destructors | |
| Tensor () | |
| Default constructor for Tensor. | |
| Tensor (const shape_type &shape, bool requires_grad=false) | |
| Constructor that initializes a Tensor with the specified shape. | |
| Tensor (const shape_type &shape, value_type *data, bool requires_grad=false, bool host=true) | |
| Constructs a Tensor object with specified shape, data, gradient requirement, and data location. | |
| Tensor (const shape_type &shape, const std::initializer_list< value_type > &data, bool requires_grad=false) | |
| Constructs a Tensor object with a specified shape, initializer list data, and gradient requirement. | |
| Tensor (const Tensor &other) | |
| Copy constructor for Tensor. | |
| Tensor (Tensor &&other) noexcept(false) | |
| Move constructor for Tensor. | |
| Tensor & | operator= (const Tensor &other) |
| Assignment operator for Tensor. | |
| Tensor & | operator= (Tensor &&other) noexcept(false) |
| Move assignment operator for Tensor. | |
| ~Tensor () noexcept(false) | |
| Destructor for Tensor. | |
Getters and Setters | |
| bool | requiresGrad () const noexcept |
| Checks whether the tensor requires gradient computation. | |
| shape_type | shape () const noexcept |
| Retrieves the shape of the tensor. | |
| size_type | size () const noexcept |
| Retrieves the total number of elements in the tensor. | |
| void | setRequiresGrad (bool requires_grad) |
| Sets whether the tensor requires gradient computation. | |
| value_type * | data () const noexcept |
| Retrieves a pointer to the tensor's data stored in GPU memory. | |
| std::vector< value_type > | hostData () const noexcept |
| Retrieves the tensor data from the device to the host and returns it as a std::vector. | |
| value_type * | grad () const |
| Retrieves a pointer to the gradient data stored in GPU memory. | |
| std::vector< value_type > | hostGrad () const |
| Retrieves the gradient data of the tensor from the device to the host and returns it as a std::vector. | |
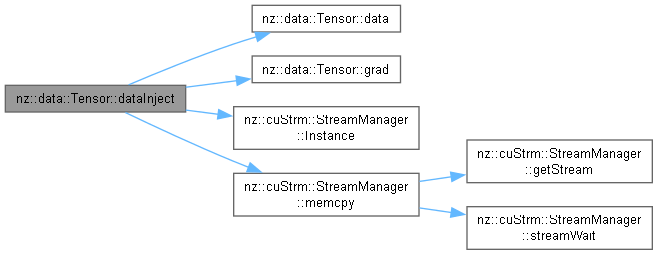
| void | dataInject (value_type *data, bool grad=false) const |
| Injects data or gradient data into the tensor. | |
| template<typename Iterator > | |
| void | dataInject (Iterator begin, Iterator end, const bool grad=false) const |
| Injects data or gradient data into the tensor using iterators. | |
| void | dataInject (const std::initializer_list< value_type > &data, bool grad=false) const |
| Injects data or gradient data into the tensor using a std::initializer_list. | |
Modifiers | |
| void | zeroGrad () const |
| Resets the gradient data to zero. | |
| void | randomize (unsigned long long seed=0) const |
| Randomizes the tensor's data with a uniform distribution. | |
| void | clear () const |
| Clears the tensor's data by setting all elements to zero. | |
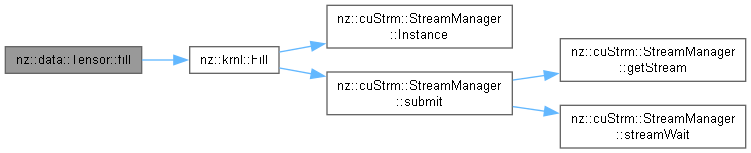
| void | fill (value_type value, bool isGrad=false) const |
| Fills the tensor's data with a specified value. | |
| void | fillMatrix (value_type value, size_type batch, size_type channels, bool isGrad=false) |
| Fill a specific matrix slice within the Tensor with a given value. | |
| void | reshape (const shape_type &shape) |
| Reshapes the tensor to the specified shape. | |
| void | transpose () |
| Transposes the tensor by swapping its dimensions and rearranging the data. | |
| void | setData (const shape_type &position, value_type value, bool isGrad=false) const |
| Sets the value of an element in the tensor or its gradient at a specified position. | |
Math | |
| Tensor | operator+ (const Tensor &other) const |
| Adds two tensors element-wise and returns the result. | |
| Tensor | operator- (const Tensor &other) const |
| Subtracts one tensor from another element-wise and returns the result. | |
| Tensor | operator* (const Tensor &other) const |
| Performs matrix multiplication of two tensors (matrices) and returns the result. | |
| Tensor | operator/ (const Tensor &other) const |
| Performs element-wise division between two Tensors. | |
| Tensor | operator- () const |
| Negates all elements of the tensor and returns the result. | |
| bool | operator== (const Tensor &other) const |
| Checks if two Tensor objects are equal. | |
| bool | operator!= (const Tensor &other) const |
| Checks if two Tensor objects are not equal. | |
| void | recip () const |
| Computes the reciprocal (1/x) of each element in the tensor and updates the tensor in-place. | |
| value_type | sum () const |
| Compute the sum of all elements in the Tensor. | |
| value_type | sum (size_type batch, size_type channel) const |
| Computes the sum of elements in a specific batch and channel of a Tensor. | |
| value_type | max () const |
| Finds the maximum value in the tensor. | |
| value_type | max (size_type batch, size_type channel) const |
| Finds the maximum value in a specific batch and channel of the tensor. | |
| value_type | min () const |
| Finds the minimum value in the entire tensor. | |
| value_type | min (size_type batch, size_type channel) const |
| Finds the minimum value in a specific batch and channel of the tensor. | |
| shape_type | find (value_type value) const |
| Finds the first occurrence of a given value in the entire tensor and returns its shape indices. | |
| shape_type | find (value_type value, size_type batch, size_type channel) const |
| Finds the first occurrence of a given value in a specific batch and channel of the tensor and returns its shape indices. | |
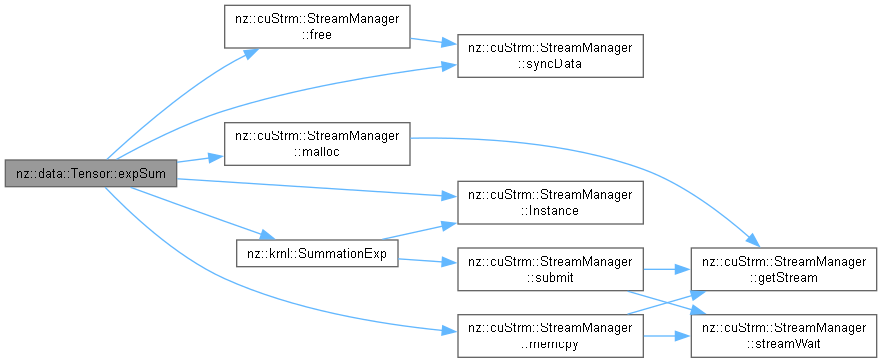
| value_type | expSum () const |
| Compute the sum of the exponential values of all elements in the Tensor. | |
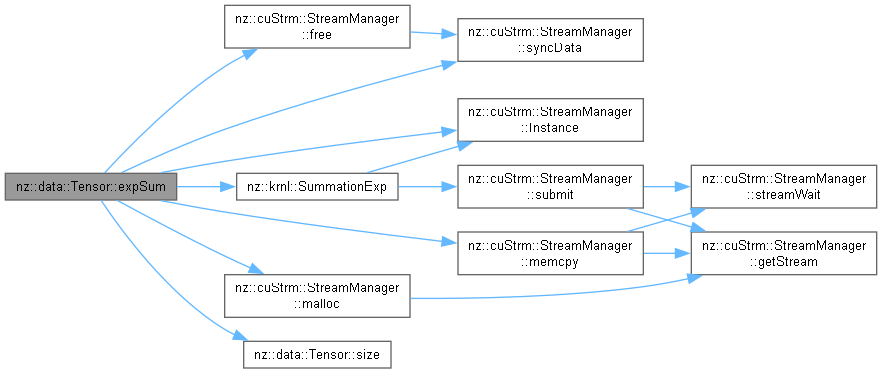
| value_type | expSum (size_t batch, size_t channel) const |
| Computes the sum of exponential values of elements in a specific batch and channel of a Tensor. | |
| void | syncData () const |
| Synchronize the tensor data by waiting for all CUDA stream write operations to complete. | |
| void | syncGrad () const |
| Synchronize the gradient data of the tensor if gradient computation is required. | |
| void | sync () const |
| Synchronize both the tensor data and its gradient data. | |
Printer | |
| std::ostream & | printGrad (std::ostream &os) const |
| Prints the gradient values of the tensor to an output stream. | |
| std::ostream & | print (std::ostream &os) const |
| Prints the tensor data to an output stream. | |
Friends | |
| DL_API std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &os, const Tensor &tensor) |
Overloads the << operator to print the tensor's data to an output stream. | |
| DL_API std::istream & | operator>> (std::istream &is, const Tensor &tensor) |
Overloads the >> operator to read a tensor's data from an input stream. | |
A class for representing and manipulating multidimensional arrays (tensors) in GPU memory.
The Tensor class is designed for high-performance numerical computations in GPU-based environments. It provides a wide range of functionalities, including tensor creation, mathematical operations, memory management, and gradient computation for deep learning tasks.
size_type: An alias for unsigned long long, used to represent the size of the tensor. Supports large tensors with up to 64-bit indices.value_type: An alias for float, representing the data type of the tensor elements. Suitable for most machine learning computations.shape_type: An alias for std::vector<int>, representing the shape of the tensor (e.g., {2, 3} for a 2x3 matrix).+, -, *, /) and activation functions (ReLU, Sigmoid, Tanh, etc.).requires_grad) to facilitate backpropagation in neural networks.Definition at line 134 of file Tensor.cuh.
| nz::data::Tensor::Tensor | ( | ) |
|
explicit |
Constructor that initializes a Tensor with the specified shape.
| shape | A vector representing the dimensions of the tensor. |
| requires_grad | A boolean indicating whether the tensor requires gradient computation. |
This constructor allocates GPU memory for the tensor based on the specified shape. If requires_grad is set to true, additional memory is allocated for storing gradients.
Definition at line 92 of file Tensor.cu.

|
explicit |
Constructs a Tensor object with specified shape, data, gradient requirement, and data location.
| shape | A reference to the shape of the tensor (host-to-device). The shape determines the size of the tensor. |
| data | A pointer to the initial data of the tensor. The data can be either on the host or device depending on the host parameter. |
| requires_grad | A boolean indicating whether the tensor requires gradient computation. |
| host | A boolean indicating whether the data pointed to by data is on the host or device. If true, data is on the host; otherwise, it is on the device. |
This constructor initializes a Tensor object. It first calculates the total size of the tensor based on the provided shape. Then, it allocates device memory for the tensor's data using cudaMalloc.
Depending on the value of the host parameter, it copies the data from either the host or another device memory location to the newly allocated device memory using cudaMemcpy.
If the requires_grad parameter is true, it also allocates device memory for the gradient data of the tensor. Otherwise, it sets the gradient pointer _grad to nullptr.
For memory management, the constructor allocates device memory for the tensor's data and gradient (if required). The responsibility of freeing this memory lies with the destructor of the Tensor class.
In terms of exception handling, this constructor does not explicitly catch any CUDA errors. If a CUDA operation fails (e.g., cudaMalloc or cudaMemcpy), it will likely lead to undefined behavior in subsequent operations. It is the caller's responsibility to check for CUDA errors using cudaGetLastError or other appropriate methods.
This constructor is a fundamental part of the Tensor class as it initializes the object's internal state.
| None | explicitly, but CUDA operations may fail and return an error code. |
data pointer is valid and points to enough data to fill the tensor according to the specified shape._size).Definition at line 104 of file Tensor.cu.
|
explicit |
Constructs a Tensor object with a specified shape, initializer list data, and gradient requirement.
| shape | A reference to the shape of the tensor (host-to-device). The shape determines the dimensions and total size of the tensor. |
| data | A std::initializer_list containing the initial data for the tensor (host-to-device). |
| requires_grad | A boolean indicating whether the tensor requires gradient computation. |
This constructor initializes a Tensor object. First, it calculates the total size of the tensor based on the provided shape. It then checks if the size of the std::initializer_list is sufficient to fill the tensor. If not, it throws a std::invalid_argument exception.
For memory management, it allocates device memory for the tensor's data using cudaMalloc. If the tensor requires gradient computation, it also allocates device memory for the gradient data; otherwise, it sets the gradient pointer to nullptr.
A temporary host buffer is created to hold the data from the std::initializer_list. The data is copied from the initializer list to the host buffer and then transferred from the host buffer to the device memory using cudaMemcpy. After the transfer, the temporary host buffer is deleted to prevent memory leaks.
Regarding exception handling, it throws a std::invalid_argument if the initializer list size is insufficient. Any CUDA errors during memory allocation or data transfer are not explicitly caught here, and it's the caller's responsibility to check for CUDA errors.
This constructor is an important part of the Tensor class as it provides a convenient way to initialize a tensor with an initializer list.
| std::invalid_argument | If the size of the std::initializer_list is less than the size of the tensor. |
Definition at line 123 of file Tensor.cu.
| nz::data::Tensor::Tensor | ( | const Tensor & | other | ) |
| nz::data::Tensor::Tensor | ( | Tensor && | other | ) |
| nz::data::Tensor::~Tensor | ( | ) |
| void nz::data::Tensor::clear | ( | ) | const |
Clears the tensor's data by setting all elements to zero.
This function resets the tensor's data to zero by filling the memory allocated for the tensor's data with zero values. It uses the cudaMemset function to set all the values in the tensor's GPU memory to zero. This is commonly used to clear or reset the tensor before using it for new computations.
Definition at line 302 of file Tensor.cu.
|
nodiscardnoexcept |
Retrieves a pointer to the tensor's data stored in GPU memory.
value_type* (pointer to float) pointing to the tensor's data in GPU memory.This function provides direct access to the raw data of the tensor stored in GPU memory. It is useful for low-level operations or when interfacing with other libraries that require access to the tensor's memory.
| void nz::data::Tensor::dataInject | ( | const std::initializer_list< value_type > & | data, |
| bool | grad = false ) const |
Injects data or gradient data into the tensor using a std::initializer_list.
| data | A std::initializer_list containing the data to be injected (host-to-device). |
| grad | A boolean indicating whether to inject gradient data. |
This function serves as a wrapper that calls another dataInject function, passing the begin and end iterators of the provided std::initializer_list. In terms of memory management, it relies on the underlying dataInject function to handle memory operations for the actual data injection. Regarding exception handling, it simply propagates any exceptions thrown by the underlying dataInject function without additional handling. This function is closely related to the Tensor class and the other dataInject functions as it leverages the existing data injection logic.
| std::runtime_error | If the length of the input array is less than the size of the tensor. |
| nz::CudaException | If the CUDA memory copy fails or if the tensor does not require gradients when trying to inject gradient data. |
std::initializer_list should contain enough elements to fill the tensor.dataInject function which is O(n) where n is the size of the tensor.Definition at line 241 of file Tensor.cu.
|
inline |
Injects data or gradient data into the tensor using iterators.
| begin | An iterator pointing to the beginning of the input data range (host-to-device). |
| end | An iterator pointing to the end of the input data range (host-to-device). |
| grad | A boolean indicating whether to inject gradient data. Defaults to false. |
This function injects data or gradient data into the tensor using the provided iterator range. First, it checks if the length of the input range (determined by std::distance(begin, end)) is at least as large as the size of the tensor (_size). If not, it throws a std::runtime_error.
For memory management, it allocates a temporary host array host_data of size _size to store the data from the iterator range. The data is then copied from the iterator range to this temporary array. After that, it calls the dataInject function with the temporary array and the grad flag.
In case of an exception during the call to the dataInject function, the temporary array is deleted to prevent memory leaks. Finally, the temporary array is deleted after the call to dataInject returns successfully.
The exception handling mechanism catches any nz::CudaException or std::runtime_error thrown by the dataInject function and re - throws it after cleaning up the temporary memory.
This function is closely related to the Tensor class and the other dataInject function as it uses the other dataInject function to perform the actual data injection.
| std::runtime_error | If the length of the input array is less than the size of the tensor. |
| nz::CudaException | If the CUDA memory copy fails or if the tensor does not require gradients when trying to inject gradient data. |
begin and end should be valid and form a proper range.value_type of the tensor._size), due to the loop that copies data from the iterator range to the temporary array.Definition at line 567 of file Tensor.cuh.
| void nz::data::Tensor::dataInject | ( | value_type * | data, |
| bool | grad = false ) const |
Injects data or gradient data into the tensor.
| data | A pointer to the data to be injected (host-to-device). |
| grad | A boolean indicating whether to inject gradient data. |
This function is responsible for injecting data or gradient data into the tensor. For memory management, it uses cudaMemcpy to copy data from the host to the device. If the grad parameter is true, it tries to copy data to the gradient buffer (_grad). If the tensor does not require gradients (_requires_grad is false), it throws an exception. If the grad parameter is false, it copies data to the main data buffer (_data).
The exception handling mechanism is in place to catch any CUDA memory copy errors. If the cudaMemcpy operation fails, it throws a nz::CudaException with an appropriate error message.
This function is closely related to the Tensor class as it modifies the internal data of the tensor.
| nz::CudaException | If the CUDA memory copy fails or if the tensor does not require gradients when trying to inject gradient data. |
data should point to a valid memory location with enough data to fill the tensor.data is less than the size of the tensor, it will lead to undefined behavior and potentially cause unknown issues in the program.Definition at line 282 of file Tensor.cu.
|
nodiscard |
Compute the sum of the exponential values of all elements in the Tensor.
Tensor::value_type.This function calculates the sum of the exponential values of all elements in the Tensor. It first configures the CUDA block and grid dimensions. Then, it allocates device memory for intermediate results and host memory to hold the copied results from the device. The krnl::SummationExp CUDA kernel is launched to compute the partial sums of the exponential values on the device. After the kernel execution, the partial sums are transferred from the device to the host using cudaMemcpy. Finally, the partial sums on the host are added together to obtain the total sum, and the allocated host and device memory are freed.
Memory management:
hData using new[] and freed using delete[].dData using cudaMalloc and freed using cudaFree.Exception handling:
CHECK macro is used to handle CUDA API errors. If a CUDA API call fails, the CHECK macro will throw an exception, and the function will terminate.Relationship with other components:
krnl::SummationExp CUDA kernel to perform the partial sums of exponential values on the device.CHECK macro to handle CUDA API errors.| [Exception | type thrown by CHECK macro] If there are CUDA API errors during memory allocation, kernel execution, or memory copying. |
_size). The CUDA kernel parallelizes the partial sum calculation of exponential values, and the final sum on the host is a linear operation over the number of grid blocks.Definition at line 694 of file Tensor.cu.
|
nodiscard |
Computes the sum of exponential values of elements in a specific batch and channel of a Tensor.
| batch | The batch index. Memory flow: host - to - device (used for index calculation on the host side). |
| channel | The channel index. Memory flow: host - to - device (used for index calculation on the host side). |
This function calculates the sum of the exponential values of elements within a particular batch and channel of a Tensor. First, it validates the provided batch and channel indices. If they are out of the valid range of the Tensor's shape, it throws a std::invalid_argument exception.
After validation, it computes the size of the region to be processed based on the Tensor's shape. It then allocates device memory for intermediate results (dData) and host memory (hData) to receive the computed values from the device. The offset in the Tensor's data is determined according to the batch and channel indices.
The krnl::SummationExp kernel is launched to compute the exponential of each element and perform partial summation on the device. The intermediate results are then copied from the device to the host. Finally, the function sums up all the intermediate results on the host, frees the allocated host and device memory, and returns the final sum.
Memory Management Strategy:
hData of size grid.x is dynamically allocated using new[] and later freed using delete[].dData is allocated using cuStrm::StreamManager<value_type>::Instance().malloc and freed using cuStrm::StreamManager<value_type>::Instance().free.Exception Handling Mechanism:
std::invalid_argument exception if the provided batch or channel indices are out of the valid range of the Tensor's shape.Relationship with Other Components:
_shape member of the Tensor class to get the shape information and strides.krnl::SummationExp kernel to perform the exponential calculation and partial summation on the device.cuStrm::StreamManager<value_type>::Instance() for CUDA memory management (malloc, memcpy, free) operations.| std::invalid_argument | If the provided batch or channel indices are out of the valid range of the Tensor's shape. |
batch and channel indices are within the valid range of the Tensor's shape to avoid exceptions.Definition at line 713 of file Tensor.cu.
| void nz::data::Tensor::fill | ( | value_type | value, |
| bool | isGrad = false ) const |
Fills the tensor's data with a specified value.
This function sets all elements in the tensor's data to the specified value. It uses the cudaMemset function to fill the GPU memory allocated for the tensor with the provided value. This is commonly used to initialize a tensor with a constant value.
| value | The value to which all elements of the tensor will be set. This value is copied to every element in the tensor's data. |
| isGrad | A boolean flag indicating whether to fill the gradients or the data. If true, gradients are filled; otherwise, data is filled (host-to-device). |
Definition at line 306 of file Tensor.cu.
| void nz::data::Tensor::fillMatrix | ( | value_type | value, |
| size_type | batch, | ||
| size_type | channels, | ||
| bool | isGrad = false ) |
Fill a specific matrix slice within the Tensor with a given value.
This method allows users to populate a particular matrix slice of the Tensor (specified by batch and channels) with a provided value. It also supports filling the gradient matrix if the Tensor requires gradient computation and the isGrad flag is set.
| value | The value used to fill the matrix slice. Memory flow: host-to-function, passed from the calling code. |
| batch | The index of the batch. Memory flow: host-to-function, passed from the calling code. |
| channels | The index of the channels. Memory flow: host-to-function, passed from the calling code. |
| isGrad | A boolean indicating whether to fill the gradient matrix. Memory flow: host-to-function, passed from the calling code. |
Memory Management Strategy:
_data or _grad buffer of the Tensor.Exception Handling Mechanism:
std::invalid_argument if the provided batch or channels indices are out of bounds.std::invalid_argument if isGrad is true but the Tensor does not require gradient computation.Relationship with Other Components:
_shape object to access tensor shape information and calculate offsets.krnl::Fill CUDA kernel to perform the actual filling operation.| std::invalid_argument | When batch or channels are out of bounds or when trying to fill gradients of a non - gradient - requiring Tensor. |
_shape[2] * _shape[3]).krnl::Fill CUDA kernel is properly implemented and the CUDA environment is set up correctly._shape object provides accurate shape and stride information.Definition at line 316 of file Tensor.cu.
|
nodiscard |
Finds the first occurrence of a given value in the entire tensor and returns its shape indices.
This function retrieves the tensor data from the device to the host, then iterates through the data to find the first element equal to the given value. Once found, it calculates the corresponding shape indices (batch, channel, height, width) and returns them.
| value | The value to search for in the tensor. Memory location: host - to - device (used for comparison). |
Tensor::shape_type object representing the shape indices (batch, channel, height, width) of the first occurrence of the given value in the tensor. Memory flow: device - to - host._size), due to the linear traversal of the tensor data.hostData().Definition at line 660 of file Tensor.cu.
|
nodiscard |
Finds the first occurrence of a given value in a specific batch and channel of the tensor and returns its shape indices.
This function first calculates the offset in the tensor data based on the provided batch and channel indices. It then retrieves the tensor data from the device to the host and iterates through the subset of data in the specified batch and channel to find the first element equal to the given value. Once found, it calculates the height and width indices and returns the complete shape indices (batch, channel, height, width).
| value | The value to search for in the tensor. Memory location: host - to - device (used for comparison). |
| batch | The batch index. Memory location: host - to - device (used for index calculation). |
| channel | The channel index. Memory location: host - to - device (used for index calculation). |
Tensor::shape_type object representing the shape indices (batch, channel, height, width) of the first occurrence of the given value in the specified batch and channel of the tensor. Memory flow: device - to - host.| std::invalid_argument | When the batch or channel index is out of bounds. |
_shape[2] * _shape[3]), due to the linear traversal of the subset of the tensor data.hostData().batch and channel indices are within the valid range of the tensor's shape to avoid unexpected behavior.Definition at line 676 of file Tensor.cu.
|
nodiscard |
Retrieves a pointer to the gradient data stored in GPU memory.
value_type* (pointer to float) pointing to the tensor's gradient data in GPU memory.This function provides access to the gradient data of the tensor, stored in GPU memory. If the tensor does not require gradient computation (requires_grad is false), the function throws a std::runtime_error.
| std::runtime_error | If the tensor does not require gradient computation. |
|
nodiscardnoexcept |
Retrieves the tensor data from the device to the host and returns it as a std::vector.
This member function is used to transfer the tensor data from the device memory to the host memory. It returns a std::vector containing the tensor data.
| None |
std::vector of Tensor::value_type containing the tensor data. Memory flow: device - to - host.Memory Management Strategy:
temp of size _size is dynamically allocated on the host using new.cudaMemcpy, a std::vector is constructed from the temporary array.temp is then deleted using delete[] to avoid memory leaks.Exception Handling Mechanism:
noexcept, meaning it does not throw any exceptions. However, if cudaMemcpy fails, it may lead to undefined behavior.Relationship with Other Components:
syncData() function to synchronize the data before the transfer.cudaMemcpy to transfer data from the device to the host._data and _size are used to access the device data and its size._size).cudaMemcpy fails, the behavior of this function is undefined. Error checking for cudaMemcpy is not performed in this function.Definition at line 436 of file Tensor.cu.
|
nodiscard |
Retrieves the gradient data of the tensor from the device to the host and returns it as a std::vector.
This member function transfers the gradient data of the tensor from the device memory to the host memory. It returns a std::vector containing the gradient data of the tensor.
| None |
std::vector of Tensor::value_type containing the gradient data. Memory flow: device - to - host.Memory Management Strategy:
temp of size _size is dynamically allocated on the host using new.cudaMemcpy, a std::vector is constructed from the temporary array.temp is then deleted using delete[] to avoid memory leaks.Exception Handling Mechanism:
std::runtime_error if the tensor does not require gradients (_requires_grad is false).cudaMemcpy fails, it may lead to undefined behavior as error - checking for cudaMemcpy is not performed in this function.Relationship with Other Components:
syncGrad() function to synchronize the gradient data before the transfer.cudaMemcpy to transfer the gradient data from the device to the host._grad and _size are used to access the device gradient data and its size.| std::runtime_error | When the tensor does not require gradients. |
_size).cudaMemcpy fails, the behavior of this function is undefined.Definition at line 452 of file Tensor.cu.
|
nodiscard |
Finds the maximum value in the tensor.
This member function retrieves the tensor data from the device to the host and then iterates through it to find the maximum value.
| None |
Tensor::value_type in the tensor. Memory flow: device - to - host._size), due to the linear traversal of the tensor data.hostData().Definition at line 608 of file Tensor.cu.
|
nodiscard |
Finds the maximum value in a specific batch and channel of the tensor.
This member function first validates the provided batch and channel indices. If they are valid, it calculates the offset in the tensor data and then finds the maximum value within that subset of the tensor.
| batch | The batch index. Memory location: host - to - device (used for index calculation). |
| channel | The channel index. Memory location: host - to - device (used for index calculation). |
Tensor::value_type in the specified batch and channel of the tensor. Memory flow: device - to - host.| std::invalid_argument | When the batch or channel index is out of bounds. |
_shape[2] * _shape[3]), due to the linear traversal of the subset of the tensor data.hostData().batch and channel indices are within the valid range of the tensor's shape to avoid exceptions.Definition at line 619 of file Tensor.cu.
|
nodiscard |
Finds the minimum value in the entire tensor.
This function retrieves the tensor data from the device to the host and iterates through it to determine the minimum value.
| None |
Tensor::value_type in the tensor. Memory flow: device - to - host._size), due to the linear traversal of the tensor data.hostData().Definition at line 634 of file Tensor.cu.
|
nodiscard |
Finds the minimum value in a specific batch and channel of the tensor.
This function first validates the provided batch and channel indices. If they are valid, it calculates the offset in the tensor data and then finds the minimum value within that subset of the tensor.
| batch | The batch index. Memory location: host - to - device (used for index calculation). |
| channel | The channel index. Memory location: host - to - device (used for index calculation). |
Tensor::value_type in the specified batch and channel of the tensor. Memory flow: device - to - host.| std::invalid_argument | When the batch or channel index is out of bounds. |
_shape[2] * _shape[3]), due to the linear traversal of the subset of the tensor data.hostData().batch and channel indices are within the valid range of the tensor's shape to avoid exceptions.Definition at line 645 of file Tensor.cu.
| bool nz::data::Tensor::operator!= | ( | const Tensor & | other | ) | const |
Checks if two Tensor objects are not equal.
| other | The other Tensor object to compare with. Memory flow: device - to - host (the comparison in the operator== function may involve data transfer from device to host). |
This function checks the inequality of two Tensor objects. It simply negates the result of the operator== function. So, it relies on the implementation of the operator== to determine the equality of the two Tensors.
Memory Management Strategy:
operator== function. This function itself does not allocate or free any memory.Exception Handling Mechanism:
operator== function. This function does not have its own exception handling mechanism.Relationship with Other Components:
operator== function of the Tensor class.operator== function, which is O(n) where n is the number of elements in the Tensor.Performs matrix multiplication of two tensors (matrices) and returns the result.
This operator performs matrix multiplication between two tensors (2D matrices) and returns a new tensor containing the result of the multiplication. The number of columns in the first tensor must match the number of rows in the second tensor for matrix multiplication to be valid.
| other | The tensor (matrix) to multiply with the current tensor. |
This function checks if the dimensions of the two tensors are compatible for matrix multiplication. If the number of columns in the current tensor does not match the number of rows in the other tensor, it throws an std::invalid_argument exception. It then creates a new tensor to hold the result of the multiplication and uses a CUDA kernel (GeneralMatrixMul) to perform the matrix multiplication in parallel on the GPU.
| std::invalid_argument | If the matrix dimensions are incompatible for multiplication. |
_shape[1]) must match the number of rows in the other tensor (other._shape[0]) for the multiplication to be valid.Definition at line 343 of file Tensor.cu.
Adds two tensors element-wise and returns the result.
This operator performs element-wise addition of two tensors and returns a new tensor containing the sum of the corresponding elements from the two input tensors.
| other | The tensor to be added to the current tensor. |
This function checks if the shapes of the two tensors match. If they do not, it throws an std::invalid_argument exception. The function then creates a new tensor to hold the result of the addition and uses a CUDA kernel (MatrixAddKernel) to compute the sum of the tensors' elements in parallel on the GPU.
| std::invalid_argument | If the shapes of the two tensors do not match. |
Definition at line 331 of file Tensor.cu.
| Tensor nz::data::Tensor::operator- | ( | ) | const |
Negates all elements of the tensor and returns the result.
This operator performs element-wise negation of the tensor, returning a new tensor that contains the negated values of the current tensor. Each element in the tensor is multiplied by -1 to compute its negation.
This function uses a CUDA kernel (Negation) to perform the negation of each element in the tensor in parallel on the GPU. The result is stored in a new tensor, which is returned.
Definition at line 498 of file Tensor.cu.
Subtracts one tensor from another element-wise and returns the result.
This operator performs element-wise subtraction of two tensors and returns a new tensor containing the result of subtracting the corresponding elements of the two input tensors.
| other | The tensor to be subtracted from the current tensor. |
This function checks if the shapes of the two tensors match. If they do not, it throws an std::invalid_argument exception. The function then creates a new tensor to hold the result of the subtraction and uses a CUDA kernel (MatrixSub) to compute the element-wise subtraction in parallel on the GPU.
| std::invalid_argument | If the shapes of the two tensors do not match. |
Definition at line 337 of file Tensor.cu.
Performs element-wise division between two Tensors.
This function overloads the division operator to perform element-wise division between the current Tensor and another Tensor. It broadcasts the shapes of the two Tensors if necessary and creates a new Tensor to store the result.
| other | The Tensor to divide the current Tensor by. Memory flow: host-to-function, as the object is passed from the calling code to the function. |
Memory Management Strategy:
result is created within the function to store the result of the division. The memory for this Tensor is managed automatically by its constructor and destructor.Exception Handling Mechanism:
_shape.Broadcast method or the tensorElementwiseDivide function may throw exceptions if there are issues with shape broadcasting or the division operation.Relationship with Other Components:
_shape.Broadcast method to handle shape broadcasting between the two Tensors.tensorElementwiseDivide function to perform the actual element-wise division operation.tensorElementwiseDivide function needs to process each element._shape.Broadcast method and the tensorElementwiseDivide function are correctly implemented.other Tensor contains zero elements, which can lead to undefined behavior.Definition at line 352 of file Tensor.cu.
Assignment operator for Tensor.
| other | The Tensor object to assign from. |
Performs a deep copy of the tensor, including its shape, data, and gradient (if applicable).
Definition at line 173 of file Tensor.cu.
| bool nz::data::Tensor::operator== | ( | const Tensor & | other | ) | const |
Checks if two Tensor objects are equal.
| other | The other Tensor object to compare with. Memory flow: device - to - host (data is copied from device to host for comparison). |
This function compares two Tensor objects for equality. First, it checks if the _requires_grad flags of the two Tensors are the same. If they differ, the function immediately returns false. Then, it compares the shapes of the two Tensors. If the shapes are not equal, the function also returns false.
After that, it allocates host memory for temporary storage of the data from the device memory of both Tensors. It copies the data from the device to the host and compares each element one by one. If any element in the data differs, it frees the allocated host memory and returns false.
If the _requires_grad flag is set to true, it repeats the same process for the gradients of the Tensors. If any element in the gradients differs, it frees the allocated host memory and returns false.
Finally, if all comparisons pass, it frees the allocated host memory and returns true.
Memory Management Strategy:
temp and temp_other of size _size are dynamically allocated on the host using new[]. They are freed using delete[] either when a difference is found or at the end of the function.Exception Handling Mechanism:
cudaMemcpy) may return error codes indicating failures. It is assumed that the calling code or the CUDA runtime will handle these errors appropriately.Relationship with Other Components:
_requires_grad, _shape, _size, _data, and _grad members of the Tensor class.cudaMemcpy) to transfer data from device to host.Definition at line 506 of file Tensor.cu.
| std::ostream & nz::data::Tensor::print | ( | std::ostream & | os | ) | const |
Prints the tensor data to an output stream.
| os | The output stream to which the tensor data will be written (host-to-host). |
This function copies the tensor data from device memory to host memory using cudaMemcpy. It then allocates memory on the host using malloc to hold the copied data. After printing the data to the output stream, it frees the allocated host memory using free. The function does not throw any exceptions under normal circumstances. If cudaMemcpy fails, the behavior depends on the CHECK macro, which is assumed to handle errors appropriately.
Definition at line 252 of file Tensor.cu.
| std::ostream & nz::data::Tensor::printGrad | ( | std::ostream & | os | ) | const |
Prints the gradient values of the tensor to an output stream.
This function prints the gradient of the tensor (_grad) to the provided output stream (os). The gradient data is first copied from GPU memory to host memory, and then it is printed in a 2D matrix format where each row represents one dimension of the gradient. Each element in the gradient is printed, separated by a space.
| os | The output stream to which the gradient will be printed. |
os), allowing for chaining of stream operations.This function performs the following steps:
std::copy to print the gradient values in a matrix format (row by row).Definition at line 464 of file Tensor.cu.
| void nz::data::Tensor::randomize | ( | unsigned long long | seed = 0 | ) | const |
Randomizes the tensor's data with a uniform distribution.
This function fills the tensor's data with random values sampled from a uniform distribution in the range [0, 1). The random number generator is initialized using the specified seed to ensure reproducibility. The function uses the curand library to generate random numbers on the GPU.
| seed | A unsigned long long value used to initialize the random number generator. The same seed will produce the same sequence of random numbers, ensuring reproducibility. |
This function performs the following steps:
curandCreateGenerator.curandSetPseudoRandomGeneratorSeed.Definition at line 298 of file Tensor.cu.

| void nz::data::Tensor::recip | ( | ) | const |
Computes the reciprocal (1/x) of each element in the tensor and updates the tensor in-place.
This function computes the reciprocal (1/x) of each element in the tensor and stores the results back into the original tensor. The operation is performed element-wise, where each element of the tensor is replaced by its reciprocal.
The function utilizes a temporary buffer allocated on the GPU to store the intermediate reciprocal values. After the computation, the updated data is copied back to the original tensor in GPU memory.
Definition at line 554 of file Tensor.cu.
|
nodiscardnoexcept |
Checks whether the tensor requires gradient computation.
true if the tensor requires gradient computation, false otherwise.This function allows you to query whether the tensor is marked for gradient tracking, which is essential for backpropagation in neural networks. By default, tensors do not require gradients unless explicitly specified during construction or via setRequiresGrad.
| void nz::data::Tensor::reshape | ( | const shape_type & | shape | ) |
Reshapes the tensor to the specified shape.
This function changes the shape of the tensor, adjusting the layout of the data in memory. If the new shape has more elements than the current shape, the extra elements will be initialized to zero. If the new shape has fewer elements, the excess elements will be discarded.
| shape | A shape_type (alias for std::vector<int>) representing the new dimensions of the tensor. The total number of elements in the new shape can be larger or smaller than the current shape. |
This function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 358 of file Tensor.cu.
| void nz::data::Tensor::setData | ( | const shape_type & | position, |
| value_type | value, | ||
| bool | isGrad = false ) const |
Sets the value of an element in the tensor or its gradient at a specified position.
This member function allows you to set the value of a specific element in the tensor or its gradient. It first validates the position and the gradient setting based on the tensor's requirements.
| position | The position in the tensor where the value will be set. Memory location: host - to - device. |
| value | The value to be set at the specified position. Memory location: host - to - device. |
| isGrad | A boolean indicating whether to set the value in the gradient or the tensor data. Memory location: host - to - device. |
Memory Management Strategy:
data of size _size is allocated on the host using malloc.cuStrm::StreamManager<value_type>::Instance().memcpy.data is freed using free to avoid memory leaks.Exception Handling Mechanism:
std::invalid_argument if the position is out of bounds of the tensor's shape.std::invalid_argument if isGrad is true but the tensor does not require gradients.cuStrm::StreamManager operations fail, it may lead to undefined behavior as error - checking is not explicitly done in this function.Relationship with Other Components:
cuStrm::StreamManager<value_type>::Instance() for memory copying and data synchronization operations._shape member variable to validate the position and calculate the index in the data array._data and _grad member variables to access the tensor data and its gradient.| std::invalid_argument | When the position is out of bounds or when trying to set the gradient of a tensor that does not require gradients. |
_size).position is within the valid range of the tensor's shape to avoid exceptions.cuStrm::StreamManager operations fail, the behavior of this function is undefined.Definition at line 410 of file Tensor.cu.
| void nz::data::Tensor::setRequiresGrad | ( | bool | requires_grad | ) |
Sets whether the tensor requires gradient computation.
| requires_grad | A boolean indicating whether gradient computation is required. |
This function allows you to enable or disable gradient tracking for the tensor. If gradient computation is enabled, additional memory may be allocated for storing gradients.
Definition at line 229 of file Tensor.cu.
|
nodiscardnoexcept |
Retrieves the shape of the tensor.
shape_type (alias for std::vector<int>) representing the dimensions of the tensor.The shape provides information about the size of each dimension in the tensor. For example, a tensor with shape {2, 3} represents a 2x3 matrix. The shape is defined during construction or reshaping of the tensor.
|
nodiscardnoexcept |
Retrieves the total number of elements in the tensor.
size_type (alias for unsigned long long) representing the total number of elements.This function calculates the product of the dimensions in the tensor's shape. For example, a tensor with shape {2, 3} will have a size of 6. This value is useful for memory allocation and tensor operations.
|
nodiscard |
Compute the sum of all elements in the Tensor.
Tensor::value_type.This function calculates the sum of all elements in the Tensor using CUDA parallel processing. It first determines the block and grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel. Then, it allocates device memory for intermediate results and host memory to store the results copied from the device. The krnl::Summation CUDA kernel is launched to perform partial sums on the device. After the kernel execution, the partial sums are copied from the device to the host using cudaMemcpy. Finally, the partial sums on the host are added together to obtain the total sum, and the allocated host and device memory are freed.
Memory management:
hData using new[] and freed using delete[].dData using cudaMalloc and freed using cudaFree.Exception handling:
CHECK macro is used to handle CUDA API errors. If a CUDA API call fails, the CHECK macro will throw an exception, and the function will terminate.Relationship with other components:
krnl::Summation CUDA kernel to perform partial sums on the device.CHECK macro to handle CUDA API errors.| [Exception | type thrown by CHECK macro] If there are CUDA API errors during memory allocation, kernel execution, or memory copying. |
_size). The CUDA kernel parallelizes the partial sum calculation, and the final sum on the host is a linear operation over the number of grid blocks.Definition at line 565 of file Tensor.cu.
|
nodiscard |
Computes the sum of elements in a specific batch and channel of a Tensor.
| batch | The batch index. This value should be within the valid range of the Tensor's batch dimension. Memory flow: host - to - device (used for index calculation on the host side). |
| channel | The channel index. This value should be within the valid range of the Tensor's channel dimension. Memory flow: host - to - device (used for index calculation on the host side). |
This function calculates the sum of elements in a particular batch and channel of a Tensor. First, it checks if the provided batch and channel indices are valid. If not, it throws a std::invalid_argument exception. Then, it calculates the size of the region to be summed based on the Tensor's shape. It allocates device memory for intermediate results and host memory to receive the intermediate results from the device. It determines the offset in the Tensor's data based on the batch and channel indices. The krnl::Summation kernel is then launched to perform the partial summation on the device. After that, the intermediate results are copied from the device to the host. Finally, the function sums up all the intermediate results on the host, frees the allocated host and device memory, and returns the final sum.
Memory Management Strategy:
hData of size grid.x is dynamically allocated using new[] and later freed using delete[].dData is allocated using cuStrm::StreamManager<value_type>::Instance().malloc and freed using cuStrm::StreamManager<value_type>::Instance().free.Exception Handling Mechanism:
std::invalid_argument exception if the provided batch or channel indices are out of the valid range of the Tensor's shape.Relationship with Other Components:
_shape member of the Tensor class to get the shape information and strides.krnl::Summation kernel to perform the partial summation on the device.cuStrm::StreamManager<value_type>::Instance() for CUDA memory management (malloc, memcpy, free) operations.| std::invalid_argument | If the provided batch or channel indices are out of the valid range of the Tensor's shape. |
batch and channel indices are within the valid range of the Tensor's shape to avoid exceptions.Definition at line 584 of file Tensor.cu.
| void nz::data::Tensor::sync | ( | ) | const |
Synchronize both the tensor data and its gradient data.
This function calls the syncData method to synchronize the tensor data and then calls the syncGrad method to synchronize the gradient data if gradient computation is required. It ensures that all CUDA stream write operations on the data and gradient (if applicable) are completed.
| None |
Memory management for the data and gradient is assumed to be handled by the syncData and syncGrad methods respectively. There is no additional memory allocation or deallocation within this function. This function does not have an explicit exception - handling mechanism. It relies on the exception - handling of the syncData and syncGrad methods to manage any errors that may occur during the synchronization process.
syncData and syncGrad methods. In the worst - case scenario, if both operations involve long - running CUDA stream write operations, it may take a significant amount of time.Definition at line 747 of file Tensor.cu.

| void nz::data::Tensor::syncData | ( | ) | const |
Synchronize the tensor data by waiting for all CUDA stream write operations to complete.
This function accesses the singleton instance of cuStrm::StreamManager specialized for the value_type of the Tensor class. It then calls the syncData method of this instance, passing the _data member of the Tensor object. This operation blocks the host until all CUDA stream write operations on the _data are finished.
| None |
Memory management for the _data is assumed to be handled elsewhere in the codebase. There is no memory allocation or deallocation within this function. This function does not have an explicit exception - handling mechanism. It relies on the syncData method of the cuStrm::StreamManager instance to manage any errors that may occur during the synchronization process.
_data to complete. In the worst - case scenario, if there are long - running write operations, it may take a significant amount of time.Definition at line 737 of file Tensor.cu.
| void nz::data::Tensor::syncGrad | ( | ) | const |
Synchronize the gradient data of the tensor if gradient computation is required.
This function first checks the _requires_grad flag of the Tensor object. If the flag is set to true, it accesses the singleton instance of cuStrm::StreamManager specialized for the value_type of the Tensor class. Then it calls the syncData method of this instance, passing the _grad member of the Tensor object. This operation blocks the host until all CUDA stream write operations on the _grad are completed.
| None |
Memory management for the _grad is assumed to be handled elsewhere in the codebase. There is no memory allocation or deallocation within this function. This function does not have an explicit exception - handling mechanism. It relies on the syncData method of the cuStrm::StreamManager instance to manage any errors that may occur during the synchronization process.
_requires_grad flag is true and the time required for the CUDA stream write operations on _grad to complete. If _requires_grad is false, the function has a constant time complexity O(1). Otherwise, in the worst - case scenario with long - running write operations, it may take a significant amount of time.Definition at line 741 of file Tensor.cu.
| void nz::data::Tensor::transpose | ( | ) |
Transposes the tensor by swapping its dimensions and rearranging the data.
This function performs a transpose on the tensor by swapping its rows and columns. For a 2D tensor (matrix), it swaps the first and second dimensions, effectively turning the rows into columns and vice versa. The tensor's data is rearranged using a temporary buffer, and the shape is updated accordingly. The data is first copied to a temporary memory space, then a CUDA kernel is used to perform the transposition.
Definition at line 385 of file Tensor.cu.
| void nz::data::Tensor::zeroGrad | ( | ) | const |
Resets the gradient data to zero.
This function sets the gradient data of the tensor to zero. It is typically used during training in neural networks to clear the gradients before the next backpropagation pass. The gradient memory will remain allocated, but its contents will be zeroed out.
requires_grad set to true, otherwise the function does nothing.Definition at line 246 of file Tensor.cu.

|
friend |
Overloads the << operator to print the tensor's data to an output stream.
This function is a friend of the Tensor class and provides an overloaded version of the output stream operator (<<) to print the contents of a tensor to the specified output stream (e.g., std::cout or a file stream).
The tensor's data is first copied from GPU memory to host memory for printing, and then the data is printed in a 2D matrix format. Each row of the tensor is printed on a new line, and each element in a row is separated by a space. Each row is enclosed in square brackets.
| os | The output stream to which the tensor will be printed. |
| tensor | The tensor whose contents will be printed. |
os) after the tensor has been printed, allowing for chaining of operations._data) directly.cudaMemcpy, which may introduce performance overhead for large tensors.
|
friend |
Overloads the >> operator to read a tensor's data from an input stream.
This function is a friend of the Tensor class and provides an overloaded version of the input stream operator (>>) to read the contents of a tensor from the specified input stream (e.g., std::cin or a file stream).
The function reads the tensor's data element by element from the input stream and stores the values in a temporary buffer. Once all the data has been read, it is copied from the host memory back into the tensor's GPU memory using cudaMemcpy.
| is | The input stream from which the tensor's data will be read. |
| tensor | The tensor to which the data will be read. |
is) after reading the tensor's data, allowing for chaining of operations.