|
NeuZephyr
Simple DL Framework
|
 |
NeuZephyr
Simple DL Framework
|
High-Performance CUDA Kernel Implementations for Tensor Computations. More...
Functions | |
| void | MatrixAdd (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *a, float *b, float *c, unsigned long long n, size_t offset_c=0, size_t offset_a=0, size_t offset_b=0) |
| Kernel function to perform matrix addition on GPU. | |
| void | MatrixAdd (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *a, float *b, float *c, unsigned long long n, const std::vector< size_t > &offset_c, const std::vector< size_t > &offset_a, const std::vector< size_t > &offset_b) |
| Kernel function to perform matrix addition on GPU. | |
| void | MatrixSub (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *a, float *b, float *c, unsigned long long n, size_t offset_c=0, size_t offset_a=0, size_t offset_b=0) |
| Kernel function to perform matrix subtraction on GPU. | |
| void | MatrixSub (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *a, float *b, float *c, unsigned long long n, const std::vector< size_t > &offset_c, const std::vector< size_t > &offset_a, const std::vector< size_t > &offset_b) |
| Kernel function to perform matrix subtraction on GPU. | |
| void | GeneralMatrixMul (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *A, float *B, float *C, unsigned long long M, unsigned long long N, unsigned long long K, size_t offset_c=0, size_t offset_a=0, size_t offset_b=0) |
| Kernel function to perform single-precision matrix multiplication on GPU using CUDA cores. | |
| void | GeneralMatrixMul (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *A, float *B, float *C, unsigned long long M, unsigned long long N, unsigned long long K, const std::vector< size_t > &offset_c, const std::vector< size_t > &offset_a, const std::vector< size_t > &offset_b) |
| Kernel function to perform single-precision matrix multiplication on GPU using CUDA cores. | |
| void | Transpose (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *d_A, float *d_B, unsigned int rows, unsigned int cols, size_t offset=0) |
| Kernel function to transpose a matrix on the GPU. | |
| void | Transpose (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *d_A, float *d_B, unsigned int rows, unsigned int cols, const std::vector< size_t > &offset) |
| Kernel function to transpose a matrix on the GPU. | |
| void | ScalarMul (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, float num, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to perform scalar multiplication on the GPU. | |
| void | ScalarDiv (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, float num, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to perform scalar division on the GPU. | |
| void | ScalarAdd (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, float num, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to add a scalar to each element of a matrix on the GPU. | |
| void | Negation (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to negate each element of a matrix on the GPU. | |
| void | Recip (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to compute the reciprocal of each element of a matrix on the GPU. | |
| void | RectifiedLinearUnit (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to apply the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activation on the GPU. | |
| void | ReLUBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *A_grad, float *A, float *B_grad, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to compute the gradient of the ReLU activation during backpropagation. | |
| void | Sigmoid (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to apply the Sigmoid activation function on the GPU. | |
| void | SigmoidBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *A_grad, float *B, float *B_grad, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to compute the gradient of the Sigmoid activation during backpropagation. | |
| void | Tanh (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to apply the Tanh activation function on the GPU. | |
| void | TanhBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *A_grad, float *B, float *B_grad, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to compute the gradient of the Tanh activation during backpropagation. | |
| void | LeakyReLU (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, unsigned long long n, float alpha=0.01f) |
| Kernel function to apply the Leaky ReLU activation function on the GPU. | |
| void | LeakyReLUBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *A_grad, float *A, float *B_grad, unsigned long long n, float alpha=0.01f) |
| Kernel function to compute the gradient of the Leaky ReLU activation during backpropagation. | |
| void | Swish (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to apply the Swish activation function on the GPU. | |
| void | SwishBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *A_grad, float *A, float *B, float *B_grad, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to compute the gradient of the Swish activation during backpropagation. | |
| void | ExponentialLinearUnit (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, unsigned long long n, float alpha=1.0f) |
| Kernel function to apply the Exponential Linear Unit (ELU) activation function on the GPU. | |
| void | ELUBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *A_grad, float *A, float *B_grad, unsigned long long n, float alpha=1.0f) |
| Kernel function to compute the gradient of the ELU activation during backpropagation. | |
| void | HardSigmoid (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, unsigned long long n, float alpha=0.2f, float beta=0.5f) |
| Kernel function to apply the Hard Sigmoid activation function on the GPU. | |
| void | HardSigmoidBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *A_grad, float *A, float *B_grad, unsigned long long n, float alpha=0.2f, float beta=0.5f) |
| Kernel function to compute the gradient of the Hard Sigmoid activation during backpropagation. | |
| void | HardSwish (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, unsigned long long n, float alpha=0.2f, float beta=0.5f) |
| Kernel function to apply the Hard Swish activation function on the GPU. | |
| void | HardSwishBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *A_grad, float *A, float *B_grad, unsigned long long n, float alpha=0.2f, float beta=0.5f) |
| Kernel function to compute the gradient of the Hard Swish activation during backpropagation. | |
| void | SummationExp (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, size_t sharedMemSize, float *out, float *g_data, unsigned long long n, size_t offset=0) |
| Kernel function to compute the summation of exponentials of each element in the input array. | |
| void | Softmax (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, float exp_sum_of_input, unsigned long long n, size_t offset=0) |
| Kernel function to apply the Softmax function on the GPU. | |
| void | SoftmaxJacobian (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to compute the Jacobian of the Softmax function. | |
| void | MeanSquaredError (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, size_t sharedMemSize, float *out, float *predict, float *real, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to compute the Mean Squared Error (MSE) loss between predicted and real values. | |
| void | MSEBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *predict, float *real, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to compute the gradient of the Mean Squared Error (MSE) loss for backpropagation. | |
| void | StochasticGradientDescent (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *data, float *grad, float lr, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to perform Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) optimization. | |
| void | BinaryCrossEntropy (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, size_t sharedMemSize, float *out, float *predict, float *real, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to compute the Binary Cross Entropy (BCE) loss between predicted and real values. | |
| void | BCEBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *predict, float *real, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to compute the gradient of Binary Cross Entropy (BCE) loss for backpropagation. | |
| void | Momentum (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *output, float *grad, float *velocity, float beta, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to apply Momentum optimization. | |
| void | AdaGrad (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *data, float *G, float *grad, float lr, float eps, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to apply AdaGrad optimization. | |
| void | RMSprop (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *data, float *v, float *grad, float lr, float beta, float eps, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to apply RMSprop optimization. | |
| void | Adam (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *data, float *m, float *v, float *grad, float lr, float beta1, float beta2, float eps, int t, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to apply Adam optimization. | |
| void | NAdam (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *data, float *m, float *m_modified, float *v, float *grad, float lr, float beta1, float beta2, float eps, int t, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to apply NAdam optimization. | |
| void | AdaDelta (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *data, float *acc_delta, float *acc_grad, float *grad, float rho, float eps, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to apply AdaDelta optimization. | |
| void | TensorCoreGEMM (float *A, float *B, float *C, unsigned long long M, unsigned long long N, unsigned long long K) |
| Kernel function to perform fast matrix multiplication using Tensor Cores with half-precision (FP16) support. | |
| void | Fill (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *data, float value, unsigned long long n, size_t offset=0) |
| Kernel function to fill a data array with a given value. | |
| void | HadamardProduct (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in1, float *in2, unsigned long long n) |
| Kernel function to perform element-wise Hadamard product of two arrays. | |
| void | ElementwiseDivide (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in1, float *in2, unsigned long long n, size_t offset_o=0, size_t offset_1=0, size_t offset_2=0) |
| Kernel function to perform element-wise division of two arrays. | |
| void | Summation (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, unsigned long long sharedMemSize, float *out, float *in, unsigned long long n, size_t offset=0) |
| Kernel function to perform element-wise summation of two arrays. | |
| void | gradCopy (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, size_t n, const std::vector< size_t > &offset_o, const std::vector< size_t > &offset_i) |
| Copies gradient data from one array to another with specified offsets. | |
| void | NgradCopy (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, size_t n, const std::vector< size_t > &offset_o, const std::vector< size_t > &offset_i) |
| Copies gradient data from one array to another with specified offsets. | |
| void | Expand (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, size_t n, size_t total) |
| Expands the input array into the output array with a specified total size. | |
| void | Compress (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, size_t n, size_t total) |
| Compresses the input array into the output array with a specified total size. | |
| void | img2col (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, size_t H_out, size_t W_out, size_t C, size_t K_h, size_t K_w, size_t stride, size_t pad, size_t H_in, size_t W_in, size_t batch) |
| Rearranges image data into column format for convolution operations. | |
| void | img2colBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, size_t H_out, size_t W_out, size_t C, size_t K_h, size_t K_w, size_t stride, size_t pad, size_t H_in, size_t W_in, size_t batch) |
| Rearranges columnar data back into image format for backpropagation in convolution operations. | |
| void | col2img (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, size_t H_out, size_t W_out, size_t C_out, size_t batches) |
| Rearranges columnar data back into image format. | |
| void | col2imgBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, size_t H_out, size_t W_out, size_t C_out, size_t batches) |
| Rearranges columnar data back into image format for backpropagation. | |
| void | AveragePooling (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, size_t pool_size, size_t stride, size_t padding, size_t batches, size_t channels, size_t H_in, size_t W_in, size_t H_out, size_t W_out) |
| Kernel function to perform average pooling on the GPU. | |
| void | AveragePoolingBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *out, float *in, size_t pool_size, size_t stride, size_t padding, size_t batches, size_t channels, size_t H_in, size_t W_in, size_t H_out, size_t W_out) |
| Kernel function to compute the gradient of average pooling during backpropagation. | |
| void | GlobalAvgPoolBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *output, float *in, size_t batches, size_t channels, size_t height, size_t width) |
| Kernel function to compute the gradient of global average pooling during backpropagation. | |
| void | MaxPooling (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *output, float *position, float *input, size_t pool_size, size_t stride, size_t padding, size_t batches, size_t channels, size_t H_in, size_t W_in, size_t H_out, size_t W_out) |
| Kernel function to perform max pooling on the GPU. | |
| void | MaxPoolingBackward (dim3 gridDim, dim3 blockDim, float *output, float *position, float *input, size_t pool_size, size_t stride, size_t padding, size_t batches, size_t channels, size_t H_in, size_t W_in, size_t H_out, size_t W_out) |
| Kernel function to compute the gradient of max pooling during backpropagation. | |
High-Performance CUDA Kernel Implementations for Tensor Computations.
The nz::krnl namespace provides an extensive collection of CUDA kernel functions optimized for accelerated tensor operations and deep learning computations.
The namespace encompasses several critical categories of computational kernels:
Linear Activations:
Non-linear Activations:
Gradient computation kernels for each activation function, supporting efficient backpropagation in neural network training.
unsigned long long for supporting large tensor dimensions| void nz::krnl::AdaDelta | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | data, | ||
| float * | acc_delta, | ||
| float * | acc_grad, | ||
| float * | grad, | ||
| float | rho, | ||
| float | eps, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to apply AdaDelta optimization.
This function updates the data array using AdaDelta optimization, which uses a moving average of squared gradients and deltas to adaptively adjust the learning rate.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| data | Pointer to the data array that will be updated |
| acc_delta | Pointer to the accumulated delta values |
| acc_grad | Pointer to the accumulated gradient squared values |
| grad | Pointer to the gradient array |
| rho | The decay rate for the moving averages (typically between 0.9 and 0.95) |
| eps | A small constant to avoid division by zero (default 1e-8) |
| n | The number of elements in the data, gradient, and accumulated values arrays |
Definition at line 815 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::AdaGrad | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | data, | ||
| float * | G, | ||
| float * | grad, | ||
| float | lr, | ||
| float | eps, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to apply AdaGrad optimization.
This function updates the data array using AdaGrad optimization, adjusting the learning rate for each parameter based on the historical gradient squared values.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| data | Pointer to the data array that will be updated |
| G | Pointer to the array of accumulated squared gradients |
| grad | Pointer to the gradient array |
| lr | The learning rate used for the gradient update |
| eps | A small constant to avoid division by zero (default 1e-8) |
| n | The number of elements in the data, gradient, and accumulated gradient arrays |
Definition at line 731 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::Adam | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | data, | ||
| float * | m, | ||
| float * | v, | ||
| float * | grad, | ||
| float | lr, | ||
| float | beta1, | ||
| float | beta2, | ||
| float | eps, | ||
| int | t, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to apply Adam optimization.
This function updates the data array using Adam optimization, which combines momentum and RMSprop to adaptively adjust the learning rates of each parameter.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| data | Pointer to the data array that will be updated |
| m | Pointer to the first moment estimate (mean of gradients) |
| v | Pointer to the second moment estimate (variance of gradients) |
| grad | Pointer to the gradient array |
| lr | The learning rate used for the gradient update |
| beta1 | The exponential decay rate for the first moment estimate (default 0.9) |
| beta2 | The exponential decay rate for the second moment estimate (default 0.999) |
| eps | A small constant to avoid division by zero (default 1e-8) |
| t | The current time step or iteration |
| n | The number of elements in the data, gradient, and moment arrays |
Definition at line 768 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::AveragePooling | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| size_t | pool_size, | ||
| size_t | stride, | ||
| size_t | padding, | ||
| size_t | batches, | ||
| size_t | channels, | ||
| size_t | H_in, | ||
| size_t | W_in, | ||
| size_t | H_out, | ||
| size_t | W_out ) |
Kernel function to perform average pooling on the GPU.
This function applies average pooling to the input tensor, reducing its spatial dimensions by computing the average value within each pooling window.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the pooled results will be stored. |
| in | Pointer to the input array containing the original data. |
| pool_size | The size of the pooling window. |
| stride | The stride of the pooling operation. |
| padding | The padding applied to the input tensor. |
| batches | The number of batches in the input tensor. |
| channels | The number of channels in the input tensor. |
| H_in | The height of the input tensor. |
| W_in | The width of the input tensor. |
| H_out | The height of the output tensor. |
| W_out | The width of the output tensor. |
Definition at line 1431 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::AveragePoolingBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| size_t | pool_size, | ||
| size_t | stride, | ||
| size_t | padding, | ||
| size_t | batches, | ||
| size_t | channels, | ||
| size_t | H_in, | ||
| size_t | W_in, | ||
| size_t | H_out, | ||
| size_t | W_out ) |
Kernel function to compute the gradient of average pooling during backpropagation.
This function computes the gradient of the average pooling operation, distributing the gradient values evenly across the pooling window.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the gradient will be stored. |
| in | Pointer to the input array containing the gradient from the next layer. |
| pool_size | The size of the pooling window. |
| stride | The stride of the pooling operation. |
| padding | The padding applied to the input tensor. |
| batches | The number of batches in the input tensor. |
| channels | The number of channels in the input tensor. |
| H_in | The height of the input tensor. |
| W_in | The width of the input tensor. |
| H_out | The height of the output tensor. |
| W_out | The width of the output tensor. |
Definition at line 1484 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::BCEBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | predict, | ||
| float * | real, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to compute the gradient of Binary Cross Entropy (BCE) loss for backpropagation.
This function computes the gradient of the Binary Cross Entropy loss between the predicted and real values for each element in the input arrays and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the BCE gradient will be stored |
| predict | Pointer to the predicted values |
| real | Pointer to the real values |
| n | The number of elements in the input arrays |
Definition at line 701 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::BinaryCrossEntropy | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| size_t | sharedMemSize, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | predict, | ||
| float * | real, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to compute the Binary Cross Entropy (BCE) loss between predicted and real values.
This function computes the Binary Cross Entropy loss between the predicted and real values for each element in the input arrays and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| sharedMemSize | The size of the shared memory buffer used by the kernel |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the BCE result will be stored |
| predict | Pointer to the predicted values |
| real | Pointer to the real values |
| n | The number of elements in the input arrays |
Definition at line 686 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::col2img | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| size_t | H_out, | ||
| size_t | W_out, | ||
| size_t | C_out, | ||
| size_t | batches ) |
Rearranges columnar data back into image format.
This kernel function transforms columnar data into its original image format. It is typically used in operations where data needs to be reconstructed from a columnar representation, such as after convolution operations.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the reconstructed image data will be stored. |
| in | Pointer to the input columnar data array. |
| H_out | The height of the output image. |
| W_out | The width of the output image. |
| C_out | The number of output channels. |
| batches | The number of images in the batch. |
Definition at line 1378 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::col2imgBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| size_t | H_out, | ||
| size_t | W_out, | ||
| size_t | C_out, | ||
| size_t | batches ) |
Rearranges columnar data back into image format for backpropagation.
This kernel function transforms columnar data back into its original image format. It is typically used during the backpropagation phase of convolutional neural networks to reconstruct the gradient of the input image.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the reconstructed image data will be stored. |
| in | Pointer to the input columnar data array. |
| H_out | The height of the output image. |
| W_out | The width of the output image. |
| C_out | The number of output channels. |
| batches | The number of images in the batch. |
Definition at line 1398 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::Compress | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| size_t | n, | ||
| size_t | total ) |
Compresses the input array into the output array with a specified total size.
This kernel function reduces the size of the input array by compressing its elements into the output array to match the specified total size.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the compressed data will be stored. |
| in | Pointer to the input array containing the original data. |
| n | The number of elements in the input array. |
| total | The total number of elements in the output array after compression. |
Definition at line 1303 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::ElementwiseDivide | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in1, | ||
| float * | in2, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| size_t | offset_o = 0, | ||
| size_t | offset_1 = 0, | ||
| size_t | offset_2 = 0 ) |
Kernel function to perform element-wise division of two arrays.
This function performs element-wise division of two input arrays and stores the result in an output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array |
| in1 | Pointer to the first input array |
| in2 | Pointerto the second input array |
| n | The number of elements in the arrays |
| offset_o | |
| offset_1 | |
| offset_2 |
Definition at line 1181 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::ELUBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | A_grad, | ||
| float * | A, | ||
| float * | B_grad, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| float | alpha = 1.0f ) |
Kernel function to compute the gradient of the ELU activation during backpropagation.
This function computes the gradient of the ELU activation function during backpropagation and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| A_grad | Pointer to the output array where the gradient result will be stored |
| A | Pointer to the input array elements (before activation) |
| B_grad | Pointer to the gradient of the next layer |
| n | The number of elements in the arrays |
| alpha | The alpha parameter used for negative values (default 1.0) |
Definition at line 388 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::Expand | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| size_t | n, | ||
| size_t | total ) |
Expands the input array into the output array with a specified total size.
This kernel function takes an input array and expands it into an output array by repeating or padding elements to match the specified total size.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the expanded data will be stored. |
| in | Pointer to the input array containing the original data. |
| n | The number of elements in the input array. |
| total | The total number of elements in the output array after expansion. |
Definition at line 1290 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::ExponentialLinearUnit | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| float | alpha = 1.0f ) |
Kernel function to apply the Exponential Linear Unit (ELU) activation function on the GPU.
This function applies the ELU activation function (x if x > 0, alpha * (exp(x) - 1) if x <= 0) to each element of the input array and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the ELU result will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| n | The number of elements in the input and output arrays |
| alpha | The alpha parameter used for negative values (default 1.0) |
Definition at line 372 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::Fill | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | data, | ||
| float | value, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| size_t | offset = 0 ) |
Kernel function to fill a data array with a given value.
This function fills a data array with a specified value.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| data | Pointer to the data array that will be filled |
| value | The value to fill the array with |
| n | The number of elements in the data array |
| offset |
Definition at line 1153 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::GeneralMatrixMul | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | A, | ||
| float * | B, | ||
| float * | C, | ||
| unsigned long long | M, | ||
| unsigned long long | N, | ||
| unsigned long long | K, | ||
| const std::vector< size_t > & | offset_c, | ||
| const std::vector< size_t > & | offset_a, | ||
| const std::vector< size_t > & | offset_b ) |
Kernel function to perform single-precision matrix multiplication on GPU using CUDA cores.
This function is designed to execute general matrix multiplication using CUDA technology, leveraging the parallel computing capabilities of the GPU for efficient processing of large datasets. It performs single-precision (FP32) matrix multiplication on the CUDA cores, taking two input arrays of floats and storing their product in a third array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| A | Pointer to the first input matrix elements stored as a one-dimensional array |
| B | Pointer to the second input matrix elements stored as a one-dimensional array |
| C | Pointer to the output matrix where the result will be stored, allocated by the caller |
| M | The number of rows in matrix A and matrix C |
| N | The number of columns in matrix B and matrix C |
| K | The number of columns in matrix A and rows in matrix B |
| offset_c | |
| offset_a | |
| offset_b |
Definition at line 114 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::GeneralMatrixMul | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | A, | ||
| float * | B, | ||
| float * | C, | ||
| unsigned long long | M, | ||
| unsigned long long | N, | ||
| unsigned long long | K, | ||
| size_t | offset_c = 0, | ||
| size_t | offset_a = 0, | ||
| size_t | offset_b = 0 ) |
Kernel function to perform single-precision matrix multiplication on GPU using CUDA cores.
This function is designed to execute general matrix multiplication using CUDA technology, leveraging the parallel computing capabilities of the GPU for efficient processing of large datasets. It performs single-precision (FP32) matrix multiplication on the CUDA cores, taking two input arrays of floats and storing their product in a third array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| A | Pointer to the first input matrix elements stored as a one-dimensional array |
| B | Pointer to the second input matrix elements stored as a one-dimensional array |
| C | Pointer to the output matrix where the result will be stored, allocated by the caller |
| M | The number of rows in matrix A and matrix C |
| N | The number of columns in matrix B and matrix C |
| K | The number of columns in matrix A and rows in matrix B |
| offset_c | |
| offset_a | |
| offset_b |
Definition at line 103 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::GlobalAvgPoolBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | output, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| size_t | batches, | ||
| size_t | channels, | ||
| size_t | height, | ||
| size_t | width ) |
Kernel function to compute the gradient of global average pooling during backpropagation.
This function computes the gradient of the global average pooling operation, distributing the gradient values evenly across all spatial dimensions.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| output | Pointer to the output array where the gradient will be stored. |
| in | Pointer to the input array containing the gradient from the next layer. |
| batches | The number of batches in the input tensor. |
| channels | The number of channels in the input tensor. |
| height | The height of the input tensor. |
| width | The width of the input tensor. |
Definition at line 1502 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::gradCopy | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| size_t | n, | ||
| const std::vector< size_t > & | offset_o, | ||
| const std::vector< size_t > & | offset_i ) |
Copies gradient data from one array to another with specified offsets.
This kernel function performs a gradient copy operation, transferring data from the input array to the output array while applying offsets for both the input and output arrays.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the gradient data will be stored. |
| in | Pointer to the input array containing the gradient data to be copied. |
| n | The number of elements to copy. |
| offset_o | A vector of offsets for the output array. |
| offset_i | A vector of offsets for the input array. |
Definition at line 1238 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::HadamardProduct | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in1, | ||
| float * | in2, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to perform element-wise Hadamard product of two arrays.
This function performs element-wise Hadamard product of two input arrays and stores the result in an output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array |
| in1 | Pointer to the first input array |
| in2 | Pointerto the second input array |
| n | The number of elements in the arrays |
Definition at line 1165 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::HardSigmoid | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| float | alpha = 0.2f, | ||
| float | beta = 0.5f ) |
Kernel function to apply the Hard Sigmoid activation function on the GPU.
This function applies the Hard Sigmoid activation function (min(max(alpha * x + beta, 0), 1)) to each element of the input array and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the Hard Sigmoid result will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| n | The number of elements in the input and output arrays |
| alpha | The slope of the Hard Sigmoid (default 0.2) |
| beta | The offset of the Hard Sigmoid (default 0.5) |
Definition at line 403 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::HardSigmoidBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | A_grad, | ||
| float * | A, | ||
| float * | B_grad, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| float | alpha = 0.2f, | ||
| float | beta = 0.5f ) |
Kernel function to compute the gradient of the Hard Sigmoid activation during backpropagation.
This function computes the gradient of the Hard Sigmoid activation function during backpropagation and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| A_grad | Pointer to the output array where the gradient result will be stored |
| A | Pointer to the input array elements (before activation) |
| B_grad | Pointer to the gradient of the next layer |
| n | The number of elements in the arrays |
| alpha | The slope of the Hard Sigmoid (default 0.2) |
| beta | The offset of the Hard Sigmoid (default 0.5) |
Definition at line 424 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::HardSwish | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| float | alpha = 0.2f, | ||
| float | beta = 0.5f ) |
Kernel function to apply the Hard Swish activation function on the GPU.
This function applies the Hard Swish activation function (x * HardSigmoid(x)) to each element of the input array and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the Hard Swish result will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| n | The number of elements in the input and output arrays |
| alpha | The slope of the Hard Sigmoid (default 0.2) |
| beta | The offset of the Hard Sigmoid (default 0.5) |
Definition at line 445 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::HardSwishBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | A_grad, | ||
| float * | A, | ||
| float * | B_grad, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| float | alpha = 0.2f, | ||
| float | beta = 0.5f ) |
Kernel function to compute the gradient of the Hard Swish activation during backpropagation.
This function computes the gradient of the Hard Swish activation function during backpropagation and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| A_grad | Pointer to the output array where the gradient result will be stored |
| A | Pointer to the input array elements (before activation) |
| B_grad | Pointer to the gradient of the next layer |
| n | The number of elements in the arrays |
| alpha | The slope of the Hard Sigmoid (default 0.2) |
| beta | The offset of the Hard Sigmoid (default 0.5) |
Definition at line 462 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::img2col | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| size_t | H_out, | ||
| size_t | W_out, | ||
| size_t | C, | ||
| size_t | K_h, | ||
| size_t | K_w, | ||
| size_t | stride, | ||
| size_t | pad, | ||
| size_t | H_in, | ||
| size_t | W_in, | ||
| size_t | batch ) |
Rearranges image data into column format for convolution operations.
This kernel function transforms the input image data into a columnar format (im2col) to facilitate efficient convolution operations. It extracts patches from the input image based on the kernel size, stride, and padding, and stores them in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the columnar data will be stored. |
| in | Pointer to the input image data array. |
| H_out | The height of the output feature map. |
| W_out | The width of the output feature map. |
| C | The number of input channels. |
| K_h | The height of the convolution kernel. |
| K_w | The width of the convolution kernel. |
| stride | The stride of the convolution operation. |
| pad | The padding applied to the input image. |
| H_in | The height of the input image. |
| W_in | The width of the input image. |
| batch | The number of images in the batch. |
Definition at line 1330 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::img2colBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| size_t | H_out, | ||
| size_t | W_out, | ||
| size_t | C, | ||
| size_t | K_h, | ||
| size_t | K_w, | ||
| size_t | stride, | ||
| size_t | pad, | ||
| size_t | H_in, | ||
| size_t | W_in, | ||
| size_t | batch ) |
Rearranges columnar data back into image format for backpropagation in convolution operations.
This kernel function performs the reverse operation of img2col, transforming columnar data back into its original image format. It is used during the backpropagation phase of convolutional neural networks to reconstruct the gradient of the input image.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the reconstructed image data will be stored. |
| in | Pointer to the input columnar data array. |
| H_out | The height of the output feature map. |
| W_out | The width of the output feature map. |
| C | The number of input channels. |
| K_h | The height of the convolution kernel. |
| K_w | The width of the convolution kernel. |
| stride | The stride of the convolution operation. |
| pad | The padding applied to the input image. |
| H_in | The height of the input image. |
| W_in | The width of the input image. |
| batch | The number of images in the batch. |
Definition at line 1357 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::LeakyReLU | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| float | alpha = 0.01f ) |
Kernel function to apply the Leaky ReLU activation function on the GPU.
This function applies the Leaky ReLU activation function (max(alpha * x, x)) to each element of the input array and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the Leaky ReLU result will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| n | The number of elements in the input and output arrays |
| alpha | The slope of the negative part of the Leaky ReLU (default 0.01) |
Definition at line 315 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::LeakyReLUBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | A_grad, | ||
| float * | A, | ||
| float * | B_grad, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| float | alpha = 0.01f ) |
Kernel function to compute the gradient of the Leaky ReLU activation during backpropagation.
This function computes the gradient of the Leaky ReLU activation function during backpropagation (dL/dx = dL/dy * (x > 0 ? 1 : alpha)) and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| A_grad | Pointer to the output array where the gradient result will be stored |
| A | Pointer to the input array elements (before activation) |
| B_grad | Pointer to the gradient of the next layer |
| n | The number of elements in the arrays |
| alpha | The slope of the negative part of the Leaky ReLU (default 0.01) |
Definition at line 330 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::MatrixAdd | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | a, | ||
| float * | b, | ||
| float * | c, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| const std::vector< size_t > & | offset_c, | ||
| const std::vector< size_t > & | offset_a, | ||
| const std::vector< size_t > & | offset_b ) |
Kernel function to perform matrix addition on GPU.
This function is designed to execute matrix addition using CUDA technology, leveraging parallel computing capabilities of the GPU for efficient processing of large datasets. It takes two input arrays of floats and stores their sum in a third array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| a | Pointer to the first input matrix elements stored as a one-dimensional array |
| b | Pointer to the second input matrix elements stored as a one-dimensional array |
| c | Pointer to the output matrix where the result will be stored, allocated by the caller |
| n | The size of the matrix, representing the number of elements along one dimension (for a square matrix, total elements are n*n) |
| offset_c | |
| offset_a | |
| offset_b |
Definition at line 32 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::MatrixAdd | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | a, | ||
| float * | b, | ||
| float * | c, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| size_t | offset_c = 0, | ||
| size_t | offset_a = 0, | ||
| size_t | offset_b = 0 ) |
Kernel function to perform matrix addition on GPU.
This function is designed to execute matrix addition using CUDA technology, leveraging parallel computing capabilities of the GPU for efficient processing of large datasets. It takes two input arrays of floats and stores their sum in a third array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| a | Pointer to the first input matrix elements stored as a one-dimensional array |
| b | Pointer to the second input matrix elements stored as a one-dimensional array |
| c | Pointer to the output matrix where the result will be stored, allocated by the caller |
| n | The size of the matrix, representing the number of elements along one dimension (for a square matrix, total elements are n*n) |
| offset_c | |
| offset_a | |
| offset_b |
Definition at line 26 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::MatrixSub | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | a, | ||
| float * | b, | ||
| float * | c, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| const std::vector< size_t > & | offset_c, | ||
| const std::vector< size_t > & | offset_a, | ||
| const std::vector< size_t > & | offset_b ) |
Kernel function to perform matrix subtraction on GPU.
This function is designed to execute matrix subtraction using CUDA technology, leveraging parallel computing capabilities of the GPU for efficient processing of large datasets. It takes two input arrays of floats and stores their difference in a third array.
| gridDim | |
| blockDim | |
| a | Pointer to the first input matrix elements stored as a one-dimensional array |
| b | Pointer to the second input matrix elements stored as a one-dimensional array |
| c | Pointer to the output matrix where the result will be stored, allocated by the caller |
| n | The size of the matrix, representing the number of elements along one dimension (for a square matrix, total elements are n*n) |
| offset_c | |
| offset_a | |
| offset_b |
Definition at line 58 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::MatrixSub | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | a, | ||
| float * | b, | ||
| float * | c, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| size_t | offset_c = 0, | ||
| size_t | offset_a = 0, | ||
| size_t | offset_b = 0 ) |
Kernel function to perform matrix subtraction on GPU.
This function is designed to execute matrix subtraction using CUDA technology, leveraging parallel computing capabilities of the GPU for efficient processing of large datasets. It takes two input arrays of floats and stores their difference in a third array.
| gridDim | |
| blockDim | |
| a | Pointer to the first input matrix elements stored as a one-dimensional array |
| b | Pointer to the second input matrix elements stored as a one-dimensional array |
| c | Pointer to the output matrix where the result will be stored, allocated by the caller |
| n | The size of the matrix, representing the number of elements along one dimension (for a square matrix, total elements are n*n) |
| offset_c | |
| offset_a | |
| offset_b |
Definition at line 50 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::MaxPooling | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | output, | ||
| float * | position, | ||
| float * | input, | ||
| size_t | pool_size, | ||
| size_t | stride, | ||
| size_t | padding, | ||
| size_t | batches, | ||
| size_t | channels, | ||
| size_t | H_in, | ||
| size_t | W_in, | ||
| size_t | H_out, | ||
| size_t | W_out ) |
Kernel function to perform max pooling on the GPU.
This function applies max pooling to the input tensor, reducing its spatial dimensions by selecting the maximum value within each pooling window.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| output | Pointer to the output array where the pooled results will be stored. |
| position | Pointer to the array where the positions of the maximum values will be stored. |
| input | Pointer to the input array containing the original data. |
| pool_size | The size of the pooling window. |
| stride | The stride of the pooling operation. |
| padding | The padding applied to the input tensor. |
| batches | The number of batches in the input tensor. |
| channels | The number of channels in the input tensor. |
| H_in | The height of the input tensor. |
| W_in | The width of the input tensor. |
| H_out | The height of the output tensor. |
| W_out | The width of the output tensor. |
Definition at line 1539 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::MaxPoolingBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | output, | ||
| float * | position, | ||
| float * | input, | ||
| size_t | pool_size, | ||
| size_t | stride, | ||
| size_t | padding, | ||
| size_t | batches, | ||
| size_t | channels, | ||
| size_t | H_in, | ||
| size_t | W_in, | ||
| size_t | H_out, | ||
| size_t | W_out ) |
Kernel function to compute the gradient of max pooling during backpropagation.
This function computes the gradient of the max pooling operation, propagating the gradient values only to the positions of the maximum values in the pooling window.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| output | Pointer to the output array where the gradient will be stored. |
| position | Pointer to the array containing the positions of the maximum values. |
| input | Pointer to the input array containing the gradient from the next layer. |
| pool_size | The size of the pooling window. |
| stride | The stride of the pooling operation. |
| padding | The padding applied to the input tensor. |
| batches | The number of batches in the input tensor. |
| channels | The number of channels in the input tensor. |
| H_in | The height of the input tensor. |
| W_in | The width of the input tensor. |
| H_out | The height of the output tensor. |
| W_out | The width of the output tensor. |
Definition at line 1567 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::MeanSquaredError | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| size_t | sharedMemSize, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | predict, | ||
| float * | real, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to compute the Mean Squared Error (MSE) loss between predicted and real values.
This function computes the Mean Squared Error loss between the predicted and real values for each element in the input arrays and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| sharedMemSize | The size of the shared memory buffer used by the kernel |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the MSE result will be stored |
| predict | Pointer to the predicted values |
| real | Pointer to the real values |
| n | The number of elements in the input arrays |
Definition at line 615 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::Momentum | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | output, | ||
| float * | grad, | ||
| float * | velocity, | ||
| float | beta, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to apply Momentum optimization.
This function updates the output array using the Momentum optimization method, which incorporates the previous velocity to smooth the gradient update.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| output | Pointer to the output array that will be updated |
| grad | Pointer to the gradient array |
| velocity | Pointer to the previous velocity array |
| beta | The momentum factor (typically between 0.9 and 0.99) |
| n | The number of elements in the output, gradient, and velocity arrays |
Definition at line 715 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::MSEBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | predict, | ||
| float * | real, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to compute the gradient of the Mean Squared Error (MSE) loss for backpropagation.
This function computes the gradient of the Mean Squared Error loss between the predicted and real values for each element in the input arrays and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the MSE gradient will be stored |
| predict | Pointer to the predicted values |
| real | Pointer to the real values |
| n | The number of elements in the input arrays |
Definition at line 629 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::NAdam | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | data, | ||
| float * | m, | ||
| float * | m_modified, | ||
| float * | v, | ||
| float * | grad, | ||
| float | lr, | ||
| float | beta1, | ||
| float | beta2, | ||
| float | eps, | ||
| int | t, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to apply NAdam optimization.
This function updates the data array using NAdam optimization, which combines Adam with Nesterov momentum.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| data | Pointer to the data array that will be updated |
| m | Pointer to the first moment estimate (mean of gradients) |
| m_modified | Pointer to the modified first moment estimate for Nesterov momentum |
| v | Pointer to the second moment estimate (variance of gradients) |
| grad | Pointer to the gradient array |
| lr | The learning rate used for the gradient update |
| beta1 | The exponential decay rate for the first moment estimate (default 0.9) |
| beta2 | The exponential decay rate for the second moment estimate (default 0.999) |
| eps | A small constant to avoid division by zero (default 1e-8) |
| t | The current time step or iteration |
| n | The number of elements in the data, gradient, and moment arrays |
Definition at line 793 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::Negation | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to negate each element of a matrix on the GPU.
This function negates each element of the input array and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the negated result will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| n | The number of elements in the input and output arrays |
Definition at line 209 of file OperationKernels.cu.
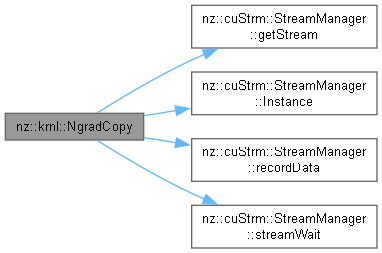
| void nz::krnl::NgradCopy | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| size_t | n, | ||
| const std::vector< size_t > & | offset_o, | ||
| const std::vector< size_t > & | offset_i ) |
Copies gradient data from one array to another with specified offsets.
This kernel function performs a gradient copy operation, transferring data from the input array to the output array while applying offsets for both the input and output arrays.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration. |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the gradient data will be stored. |
| in | Pointer to the input array containing the gradient data to be copied. |
| n | The number of elements to copy. |
| offset_o | A vector of offsets for the output array. |
| offset_i | A vector of offsets for the input array. |
Definition at line 1264 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::Recip | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to compute the reciprocal of each element of a matrix on the GPU.
This function computes the reciprocal (1/x) of each element of the input array and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the reciprocal result will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| n | The number of elements in the input and output arrays |
Definition at line 226 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::RectifiedLinearUnit | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to apply the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activation on the GPU.
This function applies the ReLU activation function (max(0, x)) to each element of the input array and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the ReLU result will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| n | The number of elements in the input and output arrays |
Definition at line 237 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::ReLUBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | A_grad, | ||
| float * | A, | ||
| float * | B_grad, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to compute the gradient of the ReLU activation during backpropagation.
This function computes the gradient of the ReLU activation function during backpropagation (dL/dx = dL/dy * (x > 0)) and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| A_grad | Pointer to the output array where the gradient result will be stored |
| A | Pointer to the input array elements (before activation) |
| B_grad | Pointer to the gradient of the next layer |
| n | The number of elements in the arrays |
Definition at line 250 of file OperationKernels.cu.

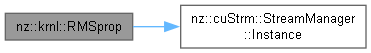
| void nz::krnl::RMSprop | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | data, | ||
| float * | v, | ||
| float * | grad, | ||
| float | lr, | ||
| float | beta, | ||
| float | eps, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to apply RMSprop optimization.
This function updates the data array using RMSprop optimization, which divides the gradient by the moving average of the squared gradient values.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| data | Pointer to the data array that will be updated |
| v | Pointer to the array of accumulated squared gradients |
| grad | Pointer to the gradient array |
| lr | The learning rate used for the gradient update |
| beta | The smoothing factor (typically between 0.9 and 0.99) |
| eps | A small constant to avoid division by zero (default 1e-8) |
| n | The number of elements in the data, gradient, and accumulated squared gradient arrays |
Definition at line 747 of file OperationKernels.cu.
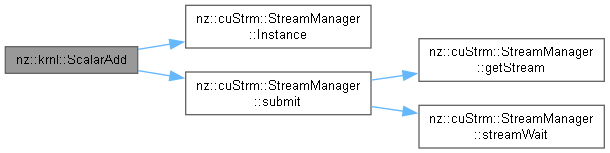
| void nz::krnl::ScalarAdd | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| float | num, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to add a scalar to each element of a matrix on the GPU.
This function adds a scalar value to each element of the input array and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the result will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| num | The scalar value to add to each element of the input array |
| n | The number of elements in the input and output arrays |
Definition at line 196 of file OperationKernels.cu.
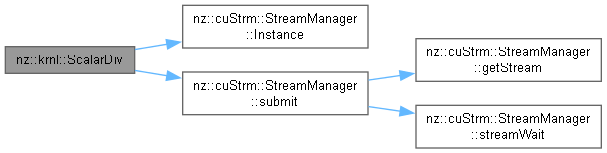
| void nz::krnl::ScalarDiv | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| float | num, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to perform scalar division on the GPU.
This function divides each element of the input array by a scalar value and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the result will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| num | The scalar value to divide each element of the input array by |
| n | The number of elements in the input and output arrays |
Definition at line 183 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::ScalarMul | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| float | num, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to perform scalar multiplication on the GPU.
This function multiplies each element of the input array by a scalar value and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the result will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| num | The scalar value to multiply each element of the input array by |
| n | The number of elements in the input and output arrays |
Definition at line 170 of file OperationKernels.cu.
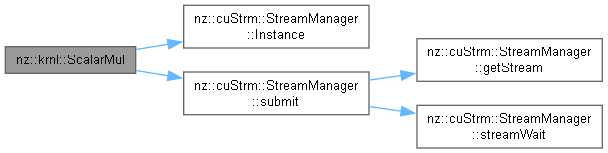
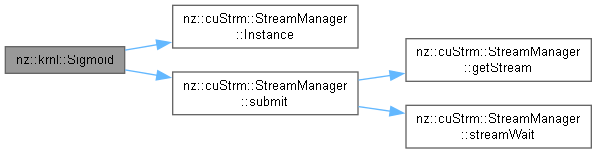
| void nz::krnl::Sigmoid | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to apply the Sigmoid activation function on the GPU.
This function applies the Sigmoid activation function (1 / (1 + exp(-x))) to each element of the input array and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the Sigmoid result will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| n | The number of elements in the input and output arrays |
Definition at line 263 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::SigmoidBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | A_grad, | ||
| float * | B, | ||
| float * | B_grad, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to compute the gradient of the Sigmoid activation during backpropagation.
This function computes the gradient of the Sigmoid activation function during backpropagation (dL/dx = dL/dy * sigmoid(x) * (1 - sigmoid(x))) and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| A_grad | Pointer to the output array where the gradient result will be stored |
| B | Pointer to the input array elements (after activation) |
| B_grad | Pointer to the gradient of the next layer |
| n | The number of elements in the arrays |
Definition at line 277 of file OperationKernels.cu.

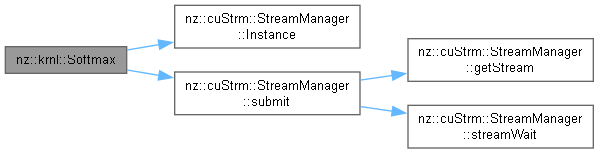
| void nz::krnl::Softmax | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| float | exp_sum_of_input, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| size_t | offset = 0 ) |
Kernel function to apply the Softmax function on the GPU.
This function applies the Softmax activation function, which normalizes the input values by exponentiating them and dividing by the sum of all exponentials, to each element of the input array and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the Softmax result will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| exp_sum_of_input | The sum of the exponentials of the input array elements |
| n | The number of elements in the input and output arrays |
| offset |
Definition at line 525 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::SoftmaxJacobian | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to compute the Jacobian of the Softmax function.
This function computes the Jacobian matrix of the Softmax function and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the Jacobian matrix will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| n | The number of elements in the input array |
Definition at line 567 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::StochasticGradientDescent | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | data, | ||
| float * | grad, | ||
| float | lr, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to perform Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) optimization.
This function updates the data array by applying Stochastic Gradient Descent with the given learning rate and gradient for each element in the input arrays.
| data | Pointer to the data array that will be updated |
| grad | Pointer to the gradient array |
| lr | The learning rate used for the gradient update |
| n | The number of elements in the data and gradient arrays |
Definition at line 642 of file OperationKernels.cu.

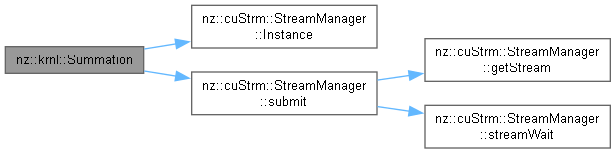
| void nz::krnl::Summation | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| unsigned long long | sharedMemSize, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| size_t | offset = 0 ) |
Kernel function to perform element-wise summation of two arrays.
This function performs element-wise summation of two input arrays and stores the result in an output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| sharedMemSize | The size of the shared memory buffer |
| out | Pointer to the output array |
| in | Pointer to the input array |
| n | The number of elements in the arrays |
| offset |
Definition at line 1225 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::SummationExp | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| size_t | sharedMemSize, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | g_data, | ||
| unsigned long long | n, | ||
| size_t | offset = 0 ) |
Kernel function to compute the summation of exponentials of each element in the input array.
This function computes the summation of exponentials of all elements in the input array and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| sharedMemSize | The size of the shared memory buffer used by the kernel |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the summation of exponentials will be stored |
| g_data | Pointer to the input array elements |
| n | The number of elements in the input array |
| offset |
Definition at line 510 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::Swish | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to apply the Swish activation function on the GPU.
This function applies the Swish activation function (x * sigmoid(x)) to each element of the input array and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the Swish result will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| n | The number of elements in the input and output arrays |
Definition at line 344 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::SwishBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | A_grad, | ||
| float * | A, | ||
| float * | B, | ||
| float * | B_grad, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to compute the gradient of the Swish activation during backpropagation.
This function computes the gradient of the Swish activation function during backpropagation and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| A_grad | Pointer to the output array where the gradient result will be stored |
| A | Pointer to the input array elements (before activation) |
| B | Pointer to the output array elements (after activation) |
| B_grad | Pointer to the gradient of the next layer |
| n | The number of elements in the arrays |
Definition at line 359 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::Tanh | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | out, | ||
| float * | in, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to apply the Tanh activation function on the GPU.
This function applies the Tanh activation function (tanh(x) = (exp(x) - exp(-x)) / (exp(x) + exp(-x))) to each element of the input array and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| out | Pointer to the output array where the Tanh result will be stored |
| in | Pointer to the input array elements |
| n | The number of elements in the input and output arrays |
Definition at line 289 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::TanhBackward | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | A_grad, | ||
| float * | B, | ||
| float * | B_grad, | ||
| unsigned long long | n ) |
Kernel function to compute the gradient of the Tanh activation during backpropagation.
This function computes the gradient of the Tanh activation function during backpropagation (dL/dx = dL/dy * (1 - tanh(x)^2)) and stores the result in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| A_grad | Pointer to the output array where the gradient result will be stored |
| B | Pointer to the input array elements (after activation) |
| B_grad | Pointer to the gradient of the next layer |
| n | The number of elements in the arrays |
Definition at line 302 of file OperationKernels.cu.

| void nz::krnl::TensorCoreGEMM | ( | float * | A, |
| float * | B, | ||
| float * | C, | ||
| unsigned long long | M, | ||
| unsigned long long | N, | ||
| unsigned long long | K ) |
Kernel function to perform fast matrix multiplication using Tensor Cores with half-precision (FP16) support.
This function performs matrix multiplication on two input matrices A and B using Tensor Cores, which are specialized hardware units in modern GPUs designed for high-throughput matrix operations. The matrices are internally padded to be multiples of 16 for efficient computation and then cropped back to their original dimensions after the operation.
| A | Pointer to the first input matrix (of size M x K) |
| B | Pointer to the second input matrix (of size K x N) |
| C | Pointer to the result matrix (of size M x N) |
| M | The number of rows in matrix A and matrix C |
| N | The number of columns in matrix B and matrix C |
| K | The number of columns in matrix A and rows in matrix B |
Definition at line 885 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::Transpose | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | d_A, | ||
| float * | d_B, | ||
| unsigned int | rows, | ||
| unsigned int | cols, | ||
| const std::vector< size_t > & | offset ) |
Kernel function to transpose a matrix on the GPU.
This function performs the transposition of a matrix on the GPU, swapping rows and columns. The resulting transposed matrix is stored in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| d_A | Pointer to the input matrix elements stored as a one-dimensional array |
| d_B | Pointer to the output matrix where the transposed result will be stored |
| rows | The number of rows in the input matrix |
| cols | The number of columns in the input matrix |
| offset | The offset within the input and output arrays |
Definition at line 154 of file OperationKernels.cu.
| void nz::krnl::Transpose | ( | dim3 | gridDim, |
| dim3 | blockDim, | ||
| float * | d_A, | ||
| float * | d_B, | ||
| unsigned int | rows, | ||
| unsigned int | cols, | ||
| size_t | offset = 0 ) |
Kernel function to transpose a matrix on the GPU.
This function performs the transposition of a matrix on the GPU, swapping rows and columns. The resulting transposed matrix is stored in the output array.
| gridDim | The grid dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| blockDim | The block dimensions for the CUDA kernel launch configuration |
| d_A | Pointer to the input matrix elements stored as a one-dimensional array |
| d_B | Pointer to the output matrix where the transposed result will be stored |
| rows | The number of rows in the input matrix |
| cols | The number of columns in the input matrix |
| offset | The offset within the input and output arrays |
Definition at line 147 of file OperationKernels.cu.