|
NeuZephyr
Simple DL Framework
|
 |
NeuZephyr
Simple DL Framework
|
Represents a scalar division operation node in a computational graph. More...
Public Member Functions | |
| ScalarDivNode (Node *input, Tensor::value_type scalar) | |
Constructor to initialize a ScalarDivNode for scalar division. | |
| void | forward () override |
Forward pass for the ScalarDivNode to perform scalar division. | |
| void | backward () override |
Backward pass for the ScalarDivNode to propagate gradients. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from nz::nodes::Node Public Member Functions inherited from nz::nodes::Node | |
| virtual void | print (std::ostream &os) const |
| Prints the type, data, and gradient of the node. | |
| void | dataInject (Tensor::value_type *data, bool grad=false) const |
| Injects data into a relevant tensor object, optionally setting its gradient requirement. | |
| template<typename Iterator > | |
| void | dataInject (Iterator begin, Iterator end, const bool grad=false) const |
| Injects data from an iterator range into the output tensor of the InputNode, optionally setting its gradient requirement. | |
| void | dataInject (const std::initializer_list< Tensor::value_type > &data, bool grad=false) const |
| Injects data from a std::initializer_list into the output tensor of the Node, optionally setting its gradient requirement. | |
Represents a scalar division operation node in a computational graph.
The ScalarDivNode class performs element-wise division of a tensor by a scalar value. It is used in computational graphs to implement normalization or scaling operations, which are fundamental in machine learning and numerical computations.
Key features:
output tensor.output tensor back to the input tensor by scaling the gradients with the reciprocal of the scalar value.output tensor.This class is part of the nz::nodes namespace and is optimized for scalar-tensor division operations in computational graphs.
| std::invalid_argument | If the scalar value is zero, as division by zero is undefined. |
| nz::nodes::calc::ScalarDivNode::ScalarDivNode | ( | Node * | input, |
| Tensor::value_type | scalar ) |
Constructor to initialize a ScalarDivNode for scalar division.
The constructor initializes a ScalarDivNode, which performs element-wise division of the output tensor of the input node by a scalar value. It validates the scalar value, sets up the node's input connections, determines the gradient tracking requirement, and prepares the output tensor with the appropriate shape and properties.
| input | A pointer to the input node. Its output tensor will be divided by the scalar value. |
| scalar | The scalar value to divide the input tensor by. |
inputs vector to establish the connection in the computational graph.output tensor with the same shape as the input tensor and determines whether the output tensor should track gradients based on the input tensor's gradient requirement.ScalarDivNode instance and used during the forward and backward passes.| std::invalid_argument | If the scalar value is zero, as division by zero is undefined. |
|
overridevirtual |
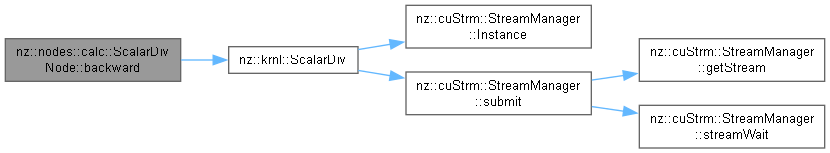
Backward pass for the ScalarDivNode to propagate gradients.
The backward() method computes the gradient of the loss with respect to the input tensor by scaling the gradient of the output tensor using the reciprocal of the scalar value. This ensures the gradients are correctly propagated back through the computational graph.
ScalarDiv) is launched to compute the scaled gradients.grad_input[i] = grad_output[i] / scalar for each element, where grad_output is the gradient of the output tensor.Implements nz::nodes::Node.
Definition at line 227 of file Nodes.cu.
|
overridevirtual |
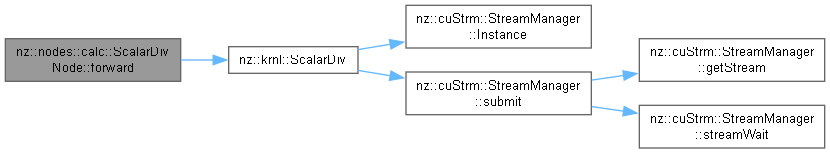
Forward pass for the ScalarDivNode to perform scalar division.
The forward() method computes the element-wise division of the input tensor by the scalar value. It uses CUDA kernels to execute the operation efficiently on the GPU.
ScalarDiv) is launched to compute the division for each element in the input tensor.output tensor.output[i] = input[i] / scalar for each element of the tensor.Implements nz::nodes::Node.
Definition at line 221 of file Nodes.cu.