|
NeuZephyr
Simple DL Framework
|
 |
NeuZephyr
Simple DL Framework
|
Represents a node that performs element-wise addition between two input tensors. More...
Public Member Functions | |
| AddNode (Node *input_left, Node *input_right) | |
Constructor to initialize an AddNode with two input nodes for element-wise addition. | |
| void | forward () override |
Forward pass for the AddNode to perform element-wise addition. | |
| void | backward () override |
Backward pass for the AddNode to propagate gradients. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from nz::nodes::Node Public Member Functions inherited from nz::nodes::Node | |
| virtual void | print (std::ostream &os) const |
| Prints the type, data, and gradient of the node. | |
| void | dataInject (Tensor::value_type *data, bool grad=false) const |
| Injects data into a relevant tensor object, optionally setting its gradient requirement. | |
| template<typename Iterator > | |
| void | dataInject (Iterator begin, Iterator end, const bool grad=false) const |
| Injects data from an iterator range into the output tensor of the InputNode, optionally setting its gradient requirement. | |
| void | dataInject (const std::initializer_list< Tensor::value_type > &data, bool grad=false) const |
| Injects data from a std::initializer_list into the output tensor of the Node, optionally setting its gradient requirement. | |
Represents a node that performs element-wise addition between two input tensors.
The AddNode class is a computational node that performs element-wise addition between two input tensors during the forward pass. It also handles the backpropagation of gradients during the backward pass, propagating the gradient of the output tensor back to both input tensors. This node is typically used to represent addition operations in neural network computations.
Key features:
forward() method performs element-wise addition of the two input tensors and stores the result in the output tensor.backward() method propagates the gradient of the output tensor to both input tensors by copying the gradient of the output to the gradients of the inputs.This class is part of the nz::nodes namespace and is designed for use in a computational graph where addition operations are needed.
AddNode is specifically for element-wise addition. The shapes of the input tensors must match.Constructor to initialize an AddNode with two input nodes for element-wise addition.
The constructor initializes an AddNode that performs element-wise addition between the outputs of two input nodes. It ensures that the shapes of the two input tensors are compatible for the addition operation. If the shapes of the two input tensors do not match, an exception is thrown. The constructor also sets up the output tensor and determines whether gradients need to be tracked based on the inputs' requiresGrad property.
| input_left | A pointer to the first input node. Its output tensor is used in the addition operation. |
| input_right | A pointer to the second input node. Its output tensor is used in the addition operation. |
The constructor verifies that the two input tensors have the same shape, and initializes the output tensor with the same shape as the inputs. The requires_grad flag for the output tensor is set to true if either of the input tensors requires gradients.
| std::invalid_argument | If the shapes of the input tensors do not match. |
output tensor is created with the same shape as the input tensors, and will track gradients if any of the input tensors require them.
|
overridevirtual |
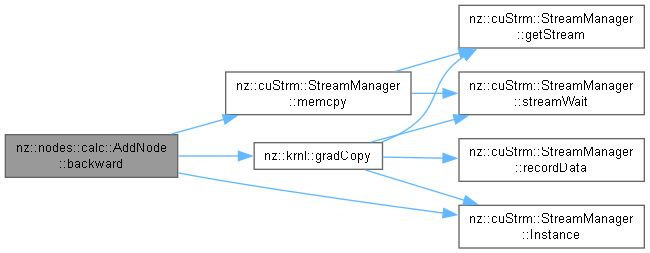
Backward pass for the AddNode to propagate gradients.
The backward() method propagates the gradient of the output tensor to the gradients of the two input tensors during the backward pass. Since addition is an element-wise operation, the gradient of the output is propagated equally to both input tensors.
If either of the input tensors requires gradients (i.e., its requiresGrad() method returns true), the gradient of the output tensor (output->grad()) is copied to the gradient of the corresponding input tensor. This is done using cudaMemcpy to efficiently propagate the gradients on the GPU.
This method is typically called during the backpropagation step of neural network training, where gradients are propagated backward through the network, starting from the output layer.
cudaMemcpy to ensure efficient GPU-based gradient propagation.Implements nz::nodes::Node.
Definition at line 99 of file Nodes.cu.
|
overridevirtual |
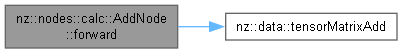
Forward pass for the AddNode to perform element-wise addition.
The forward() method performs the element-wise addition between the two input tensors and stores the result in the output tensor. It uses CUDA kernel MatrixAddKernel to carry out the addition operation efficiently on the GPU.
This method is called during the forward pass of the neural network, where it computes the sum of the two input tensors and assigns the result to the output tensor. The shape of the output tensor will be the same as the shape of the input tensors, as verified during the initialization of the AddNode.
The method divides the work into blocks and grids to parallelize the addition operation over the GPU.
MatrixAdd kernel performs the addition operation on the GPU, ensuring efficient parallel computation.output tensor is updated with the result of the addition, and it must be allocated before calling forward().Implements nz::nodes::Node.
Definition at line 95 of file Nodes.cu.